Data manipulation with dplyr
Last updated on 2026-02-03 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 65 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I add variables to my data?
- How can I alter the variables already in my data?
Objectives
- Use
mutate()to add and alter variables - Use
if_else()where appropriate - Use
case_when()where appropriate - Understand basic consents of different data types
Motivation
Often, the data we have do not contain exactly what we need. We might need to change the order of factors, create new variables based on other columns in the data, or even variables conditional on specific values in other columns.
Adding new variables,
In {tidyverse}, when we add new variables, we use the
mutate() function. Just like the other {tidyverse}
functions, mutate work specifically with data sets, and provides a nice
shorthand for working directly with the columns in the data set.
R
penguins |>
mutate(new_var = 1)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 9
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250
# ℹ 334 more rows
# ℹ 3 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>, new_var <dbl>The output of this can be hard to spot, depending on the size of the screen. Let us for convenience create a subsetted data set to work on so we can easily see what we are doing.
R
penguins_s <- penguins |>
select(1:3, starts_with("bill"))
Lets try our command again on this new data.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(new_var = 1)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 5
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm new_var
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 1
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 1
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 1
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA 1
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 1
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 1
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 1
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 1
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 1
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 1
# ℹ 334 more rowsThere is now a new column in the data set called “new_var”, and it
has the value 1 for all rows! This is what we told mutate()
to do! We specified a new column by name, and gave it a specific value,
1.
This works because its easy to assigning a single value to all rows. What if we try to give it three values? What would we expect?
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(var = 1:3)
ERROR
Error in `mutate()`:
ℹ In argument: `var = 1:3`.
Caused by error:
! `var` must be size 344 or 1, not 3.Here, it’s failing with a mysterious message. The error is telling us that input must be of size 344 or 1. 344 are the number of rows in the data set, so its telling us the input we gave it is not suitable because its neither of length 344 nor of length 1.
So now we know the premises for mutate, it takes inputs that are either of the same length as there are rows in the data set or length 1.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(var = 1:344)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 5
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm var
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 1
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 2
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 3
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA 4
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 5
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 6
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 7
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 8
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 9
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 10
# ℹ 334 more rowsBut generally, we create new columns based on other data in the data set. So let’s do a more useful example. For instance, perhaps we want to use the ratio between the bill length and depth as a measurement for a model.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(bill_ratio = bill_length_mm / bill_depth_mm)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 5
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm bill_ratio
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 2.09
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 2.27
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 2.24
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 1.90
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 1.91
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 2.19
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 2
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 1.88
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 2.08
# ℹ 334 more rowsSo, here we have asked for the ratio between bill length and depth to
be calculated and stored in a column named bill_ratio. Then
we selected just the bill columns to have a peak at the
output more directly.
We can do almost anything within a mutate() to get the
values as we want them, also use functions that exist in R to transform
the data. For instance, perhaps we want to scale the variables of
interest to have a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1, which is quite
common to improve statistical modelling. We can do that with the
scale() function.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(bill_ratio = bill_length_mm / bill_depth_mm,
bill_length_mm_z = scale(bill_length_mm))
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 6
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm bill_ratio bill_length_mm_z[,1]
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Adelie Torgers… 39.1 18.7 2.09 -0.883
2 Adelie Torgers… 39.5 17.4 2.27 -0.810
3 Adelie Torgers… 40.3 18 2.24 -0.663
4 Adelie Torgers… NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgers… 36.7 19.3 1.90 -1.32
6 Adelie Torgers… 39.3 20.6 1.91 -0.847
7 Adelie Torgers… 38.9 17.8 2.19 -0.920
8 Adelie Torgers… 39.2 19.6 2 -0.865
9 Adelie Torgers… 34.1 18.1 1.88 -1.80
10 Adelie Torgers… 42 20.2 2.08 -0.352
# ℹ 334 more rowsChallenge 1
Create a column where bill length is transformed to cm. To transform mm to cm, you must divide the mm value by 10. Name the column bill_length_cm.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(bill_length_cm = bill_length_mm / 10)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 5
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm bill_length_cm
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 3.91
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 3.95
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 4.03
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 3.67
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 3.93
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 3.89
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 3.92
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 3.41
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 4.2
# ℹ 334 more rowsChallenge 2
Create a column for body mass in kilos, rather than grams, in the main penguins data set. Name the column body_mass_kg. To transform grams to kilograms, divide the grams by 1000.
R
penguins |>
mutate(body_mass_kg = body_mass_g / 1000)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 9
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250
# ℹ 334 more rows
# ℹ 3 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>, body_mass_kg <dbl>Adding conditional variables
Sometimes, we want to assign certain data values based on other variables in the data set. For instance, maybe we want to classify all penguins with body mass above 4.5 kg as “large” while the rest are “normal”?
The if_else() function takes expressions, much like
filter(). The first value after the expression is the value
assigned if the expression is TRUE, while the second is if
the expression is FALSE
R
penguin_weight <- penguins |>
select(year, body_mass_g)
penguin_weight |>
mutate(size = if_else(condition = body_mass_g > 4500,
true = "large",
false = "normal"))
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 3
year body_mass_g size
<int> <int> <chr>
1 2007 3750 normal
2 2007 3800 normal
3 2007 3250 normal
4 2007 NA <NA>
5 2007 3450 normal
6 2007 3650 normal
7 2007 3625 normal
8 2007 4675 large
9 2007 3475 normal
10 2007 4250 normal
# ℹ 334 more rowsNow we have a column with two values, large and
normal based on whether the penguins are above or below 4.5
kilos.
We can for instance use that in a plot.
R
penguin_weight |>
mutate(size = if_else(condition = body_mass_g > 4500,
true = "large",
false = "normal")) |>
ggplot() +
geom_jitter(mapping = aes(x = year, y = body_mass_g, colour = size))
WARNING
Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).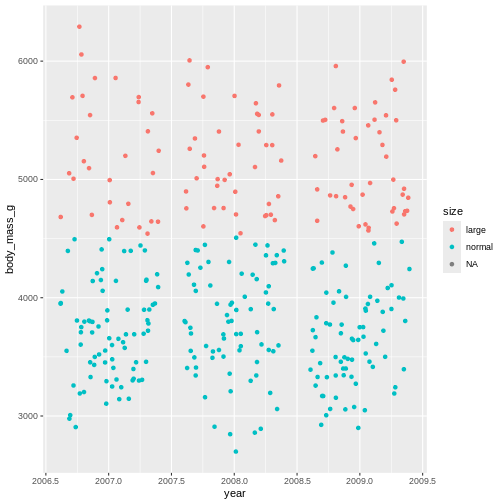
That shows us clearly that we have grouped the penguins based on
their size. But there is this strange NA in the plot
legend. what is that?
In R, missing values are usually given the value NA
which stands for Not applicable, i.e., missing
data. This is a very special name in R. Like TRUE and
FALSE are capitalized, RStudio immediately recognizes the
combination of capital letters and gives it another colour than all
other values. In this case it means, there are some penguins we do not
have the body mass of.
Now we know how to create new variables, and even how to make them if there are conditions on how to add the data.
But, we often want to add several columns of different types, and maybe even add new variables based on other new columns! Oh, it’s starting to sound complicated, but it does not have to be!
mutate() is so-called lazy-evaluated. This sounds weird,
but it means that each new column you make is made in the sequence you
make them. So as long as you think about the order of your
mutate() creations, you can do that in a single mutate
call.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(
bill_ratio = bill_depth_mm / bill_length_mm,
bill_type = if_else(condition = bill_ratio < 0.5,
true = "elongated",
false = "stumped")
)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 6
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm bill_ratio bill_type
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 0.478 elongated
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 0.441 elongated
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 0.447 elongated
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA <NA>
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 0.526 stumped
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 0.524 stumped
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 0.458 elongated
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 0.5 stumped
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 0.531 stumped
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 0.481 elongated
# ℹ 334 more rowsNow you’ve created two variables. One for bill_ratio,
and then another one conditional on the values of the
bill_ratio.
If you switched the order of these two, R would produce an error, because there would be no bill ratio to create the other column.
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(
bill_ratio = bill_depth_mm / bill_length_mm,
bill_type = if_else(condition = bill_ratio < 0.5,
true = "elongated",
false = "stumped"),
bill_ratio = bill_depth_mm / bill_length_mm
)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 6
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm bill_ratio bill_type
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 0.478 elongated
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 0.441 elongated
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 0.447 elongated
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA <NA>
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 0.526 stumped
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 0.524 stumped
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 0.458 elongated
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 0.5 stumped
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 0.531 stumped
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 0.481 elongated
# ℹ 334 more rowsBut what if we want to categorize based on more than one condition?
Nested if_else()?
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(
bill_ratio = bill_depth_mm / bill_length_mm,
bill_type = if_else(condition = bill_ratio < 0.35,
true = "elongated",
false = if_else(condition = bill_ratio < 0.45,
true = "normal",
false = "stumped")))
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 6
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm bill_ratio bill_type
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 0.478 stumped
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 0.441 normal
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 0.447 normal
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA <NA>
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 0.526 stumped
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 0.524 stumped
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 0.458 stumped
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 0.5 stumped
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 0.531 stumped
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 0.481 stumped
# ℹ 334 more rowswhat if you have even more conditionals? It can get pretty messy
pretty fast. Thankfully, {dplyr} has a smarter way of doing this, called
case_when(). This function is similar to
if_else(), but where you specify what each condition should
be assigned. On the left you have the logical expression, and the on the
right of the tilde (~) is the value to be assigned if that
expression is TRUE
R
penguins_s |>
mutate(
bill_ratio = bill_depth_mm / bill_length_mm,
bill_type = case_when(
bill_ratio < 0.35 ~ "elongated",
bill_ratio < 0.45 ~ "normal",
TRUE ~ "stumped")
) |>
ggplot(mapping = aes(x = bill_length_mm,
y = bill_depth_mm,
colour = bill_type)) +
geom_point()
WARNING
Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).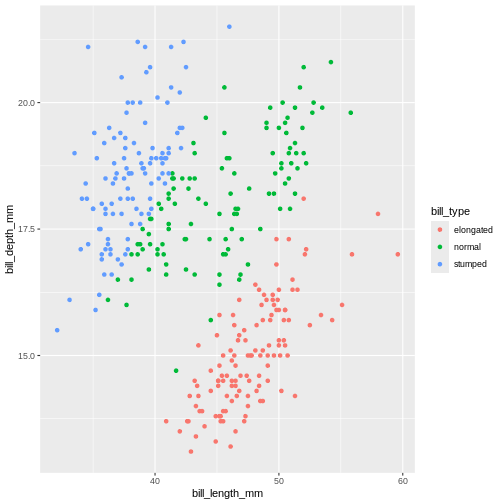
That looks almost the same. The NA’s are gone! That’s
not right. We cannot categorize values that are missing. It’s our last
statement that does this, which just says “make the remainder this
value”. Which is not what we want. We need the NAs to stay
NA’s.
case_when(), like the mutate(), evaluates
the expressions in sequence. Which is why we can have two statements
evaluating the same column with similar expressions (below 0.35 and then
below 0.45). All values that are below 0.45 are also below 0.35. Since
we first assign everything below 0.35, and then below 0.45, they do not
collide. We can do the same for our last statement, saying that all
values that are not NA should be given this category.
R
penguins |>
mutate(
bill_ratio = bill_depth_mm / bill_length_mm,
bill_type = case_when(
bill_ratio < 0.35 ~ "elongated",
bill_ratio < 0.45 ~ "normal",
!is.na(bill_ratio) ~ "stumped")
) |>
ggplot(mapping = aes(x = bill_length_mm,
y = bill_depth_mm,
colour = bill_type)) +
geom_point()
WARNING
Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).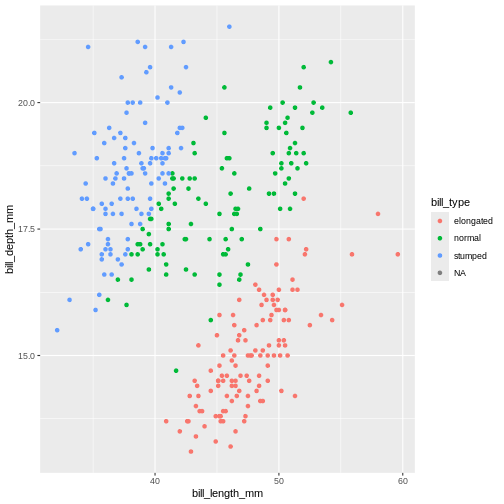
Here, we use the is.na(), which is a special function in
R to detect NA values. But it also has an ! in
front, what does that mean? In R’s logical expressions, the
! is a negation specifier. It means it flips the logical so
the TRUE becomes FALSE, and vice
versa. So here, it means the bill_ratio is
not NA.
Challenge 3
Create a column named bill_ld_ratio_log that is the
natural logarithm (using the log() function) of
bill_length_mm divided by bill_depth_mm
R
penguins |>
mutate(bill_ld_ratio_log = log(bill_length_mm / bill_depth_mm))
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 9
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250
# ℹ 334 more rows
# ℹ 3 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>, bill_ld_ratio_log <dbl>Challenge 4
Create a new column called body_type, where animals
below 3 kg are small, animals between 3 and 4.5 kg are
normal, and animals larger than 4.5 kg are
large. In the same command, create a new column named
biscoe and its content should be TRUE if the
island is Biscoe and FALSE for everything
else.
R
penguins |>
mutate(
body_type = case_when(
body_mass_g < 3000 ~ "small",
body_mass_g >= 3000 & body_mass_g < 4500 ~ "normal",
body_mass_g >= 4500 ~ "large"),
biscoe = if_else(island == "Biscoe",
true = TRUE,
false = FALSE)
)
OUTPUT
# A tibble: 344 × 10
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250
# ℹ 334 more rows
# ℹ 4 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>, body_type <chr>, biscoe <lgl>