Making Choices
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestions
How can my programs do different things based on data values?
Objectives
Write conditional statements including
if,elif, andelsebranches.Correctly evaluate expressions containing
andandor.
Conditionals
We can ask Python to take different actions, depending on a condition, with an if statement:
num = 37
if num > 100:
print('greater')
else:
print('not greater')
print('done')
not greater
done
The second line of this code uses the keyword if to tell Python that we want to make a choice.
If the test that follows the if statement is true,
the body of the if
(i.e., the set of lines indented underneath it) is executed, and “greater” is printed.
If the test is false,
the body of the else is executed instead, and “not greater” is printed.
Only one or the other is ever executed before continuing on with program execution to print “done”:
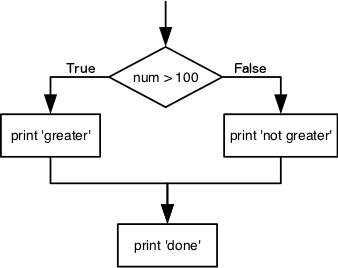
Conditional statements don’t have to include an else.
If there isn’t one,
Python simply does nothing if the test is false:
num = 53
print('before conditional...')
if num > 100:
print(num, 'is greater than 100')
print('...after conditional')
before conditional...
...after conditional
We can also chain several tests together using elif,
which is short for “else if”.
The following Python code uses elif to print the sign of a number.
num = -3
if num > 0:
print(num, 'is positive')
elif num == 0:
print(num, 'is zero')
else:
print(num, 'is negative')
-3 is negative
Note that to test for equality we use a double equals sign ==
rather than a single equals sign = which is used to assign values.
Comparing in Python
Along with the
>and==operators we have already used for comparing values in our conditionals, there are a few more options to know about:
>: greater than<: less than==: equal to!=: does not equal>=: greater than or equal to<=: less than or equal to
We can also combine tests using and and or.
and is only true if both parts are true:
if (1 > 0) and (-1 >= 0):
print('both parts are true')
else:
print('at least one part is false')
at least one part is false
while or is true if at least one part is true:
if (1 < 0) or (1 >= 0):
print('at least one test is true')
at least one test is true
TrueandFalse
TrueandFalseare special words in Python calledbooleans, which represent truth values. A statement such as1 < 0returns the valueFalse, while-1 < 0returns the valueTrue.
How Many Paths?
Consider this code:
if 4 > 5: print('A') elif 4 == 5: print('B') elif 4 < 5: print('C')Which of the following would be printed if you were to run this code? Why did you pick this answer?
- A
- B
- C
- B and C
Solution
C gets printed because the first two conditions,
4 > 5and4 == 5, are not true, but4 < 5is true.
What Is Truth?
TrueandFalsebooleans are not the only values in Python that are true and false. In fact, any value can be used in aniforelif. After reading and running the code below, explain what the rule is for which values are considered true and which are considered false.if '': print('empty string is true') if 'word': print('word is true') if []: print('empty list is true') if [1, 2, 3]: print('non-empty list is true') if 0: print('zero is true') if 1: print('one is true')
That’s Not Not What I Meant
Sometimes it is useful to check whether some condition is not true. The Boolean operator
notcan do this explicitly. After reading and running the code below, write someifstatements that usenotto test the rule that you formulated in the previous challenge.if not '': print('empty string is not true') if not 'word': print('word is not true') if not not True: print('not not True is true')
Close Enough
Write some conditions that print
Trueif the variableais within 10% of the variablebandFalseotherwise. Compare your implementation with your partner’s: do you get the same answer for all possible pairs of numbers?Hint
There is a built-in function
absthat returns the absolute value of a number:print(abs(-12))12Solution 1
a = 5 b = 5.1 if abs(a - b) <= 0.1 * abs(b): print('True') else: print('False')Solution 2
print(abs(a - b) <= 0.1 * abs(b))This works because the Booleans
TrueandFalsehave string representations which can be printed.
In-Place Operators
Python (and most other languages in the C family) provides in-place operators that work like this:
x = 1 # original value x += 1 # add one to x, assigning result back to x x *= 3 # multiply x by 3 print(x)6Write some code that sums the positive and negative numbers in a list separately, using in-place operators. Do you think the result is more or less readable than writing the same without in-place operators?
Solution
positive_sum = 0 negative_sum = 0 test_list = [3, 4, 6, 1, -1, -5, 0, 7, -8] for num in test_list: if num > 0: positive_sum += num elif num == 0: pass else: negative_sum += num print(positive_sum, negative_sum)Here
passmeans “don’t do anything”. In this particular case, it’s not actually needed, since ifnum == 0neither sum needs to change, but it illustrates the use ofelifandpass.
Counting Vowels
- Write a loop that counts the number of vowels in a character string.
- Test it on a few individual words and full sentences.
- Once you are done, compare your solution to your neighbor’s. Did you make the same decisions about how to handle the letter ‘y’ (which some people think is a vowel, and some do not)?
Solution
vowels = 'aeiouAEIOU' sentence = 'Mary had a little lamb.' count = 0 for char in sentence: if char in vowels: count += 1 print('The number of vowels in this string is ' + str(count))
Key Points
Use
if conditionto start a conditional statement,elif conditionto provide additional tests, andelseto provide a default.The bodies of the branches of conditional statements must be indented.
Use
==to test for equality.
X and Yis only true if bothXandYare true.
X or Yis true if eitherXorY, or both, are true.Zero, the empty string, and the empty list are considered false; all other numbers, strings, and lists are considered true.
TrueandFalserepresent truth values.