Wrap-up
Overview
Teaching: 15 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
Looking back at what was covered and how different pieces fit together
Where are some advanced topics and further reading available?
Objectives
Put the course in context with future learning.
Summary
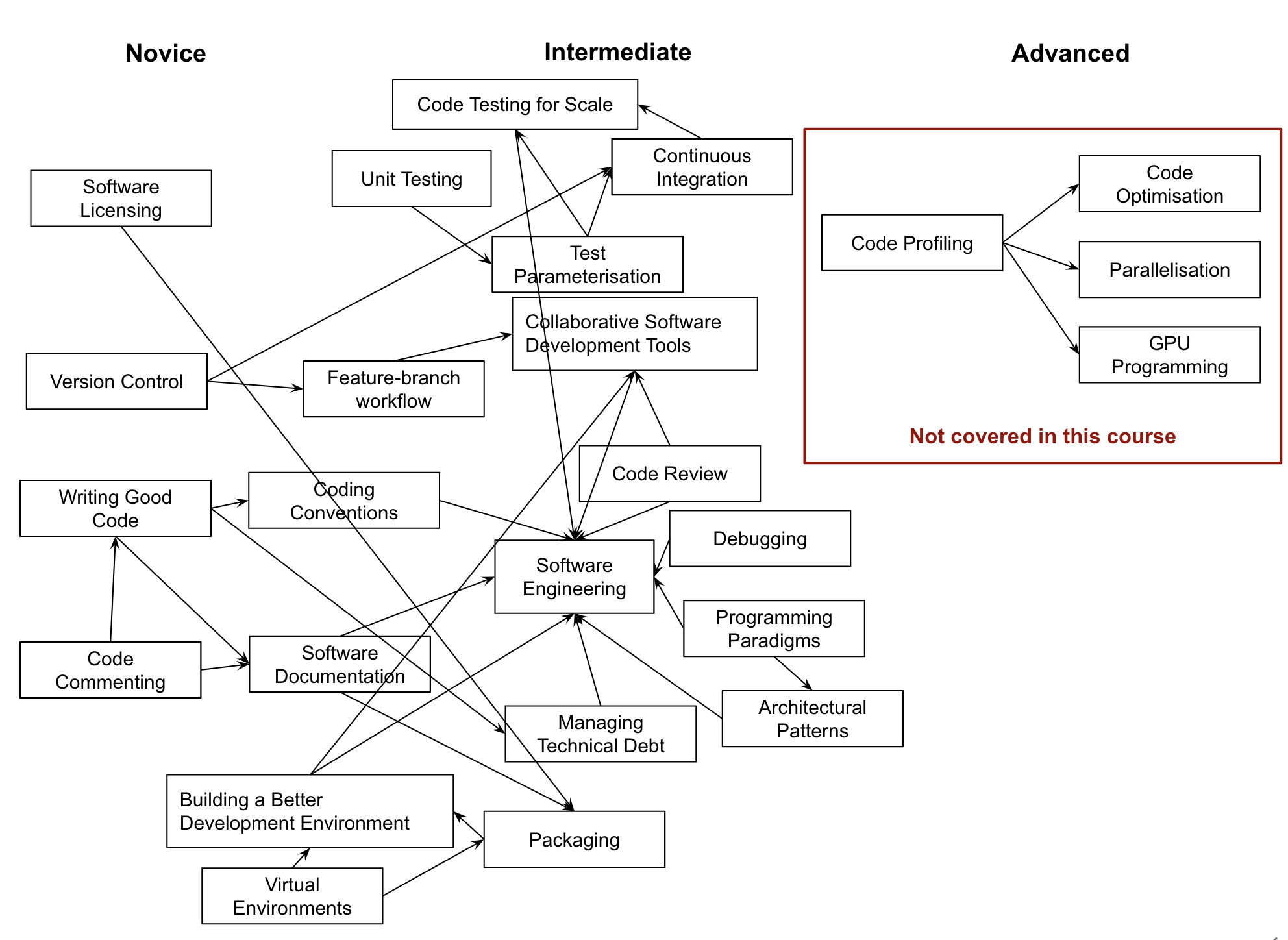
As part of this course we have looked at a core set of established, intermediate-level software development tools and best practices for working as part of a team. The course teaches a selected subset of skills that have been tried and tested in collaborative research software development environments, although not an all-encompassing set of every skill you might need (check some further reading). It will provide you with a solid basis for writing industry-grade code, which relies on the same best practices taught in this course:
- Collaborative techniques and tools play an important part of research software development in teams, but also have benefits in solo development. We’ve looked at the benefits of a well-considered development environment, using practices, tools and infrastructure to help us write code more effectively in collaboration with others.
- We’ve looked at the importance of being able to verify the correctness of software and automation, and how we can leverage techniques and infrastructure to automate and scale tasks such as testing to save us time - but automation has a role beyond simply testing: what else can you automate that would save you even more time? Once found, we’ve also examined how to locate faults in our software.
- We’ve gone beyond procedural programming and explored different software design paradigms, such as object-oriented and functional styles of programming. We’ve contrasted their pros, cons, and the situations in which they work best, and how separation of concerns through modularity and architectural design can help shape good software.
- As an intermediate developer, aspects other than technical skills become important, particularly in development teams. We’ve looked at the importance of good, consistent practices for team working, and the importance of having a self-critical mindset when developing software, and ways to manage feedback effectively and efficiently.
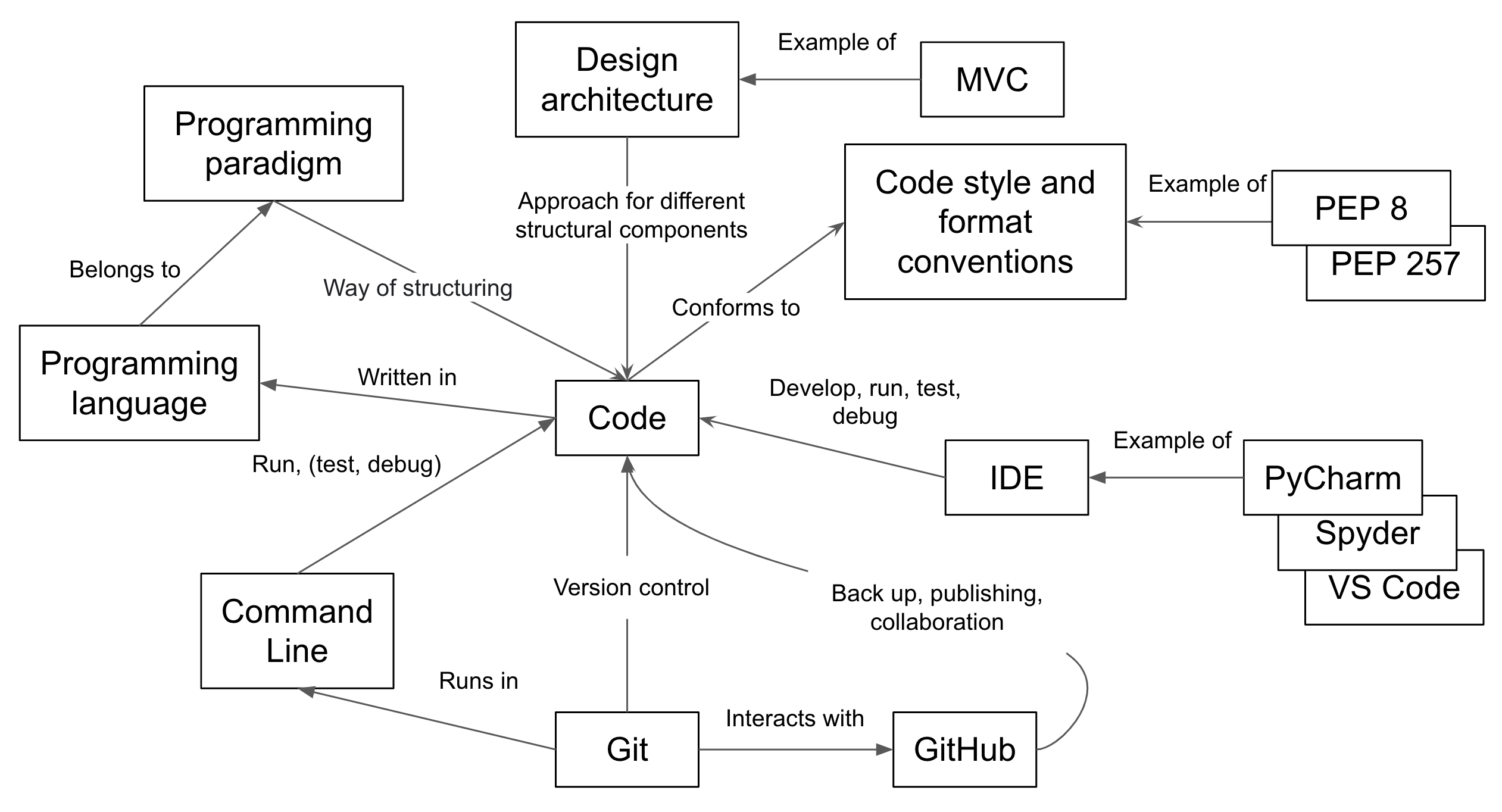
Reflection Exercise: Putting the Pieces Together
As a group, reflect on the concepts (e.g. tools, techniques and practices) covered throughout the course, how they relate to one another, how they fit together in a bigger picture or skill learning pathways and in which order you need to learn them.
Solution
Further Resources
Below are some additional resources to help you continue learning:
- Additional episode on persisting data
- Additional episode on databases
- CodeRefinery courses on FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) software practices
- Python documentation
- GitHub Actions documentation
Key Points
Collaborative techniques and tools play an important part of research software development in teams.