IntroductionGraphics Processing UnitParallel by DesignSpeed Benefits
Figure 1
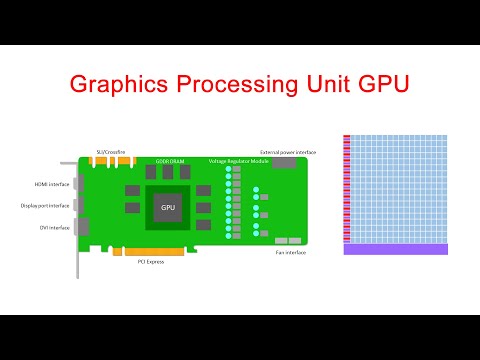
Using your GPU with CuPyIntroduction to CuPyConvolutions in PythonA scientific application: image processing for radio astronomy
Figure 1
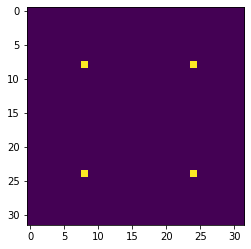
Grid of Dirac delta functions
Figure 2
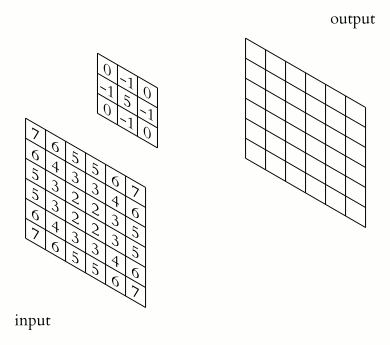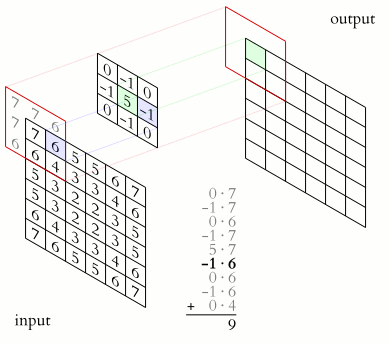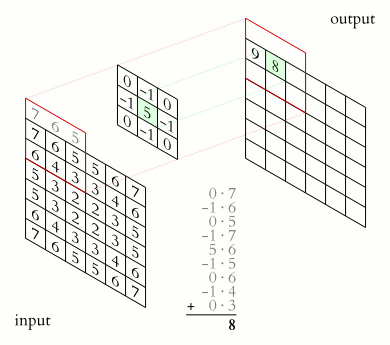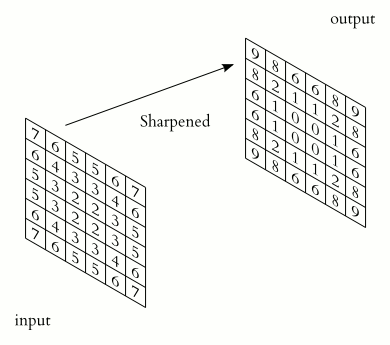
Example of animated convolution.
Figure 3
Dataflow of a map operation.
Figure 4
Dataflow of a stencil operation.
Figure 5
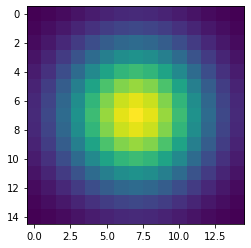
Two-dimensional Gaussian.
Figure 6
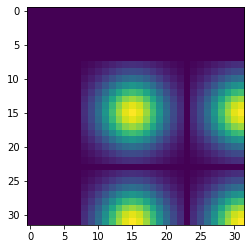
Grid of Gaussian surfaces in the convoluted
image.
Figure 7
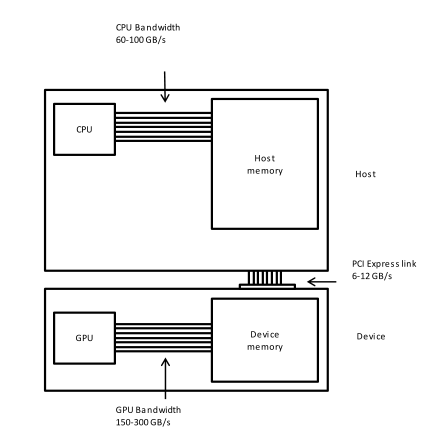
CPU and GPU are separate entities with an own
memory.
Figure 8
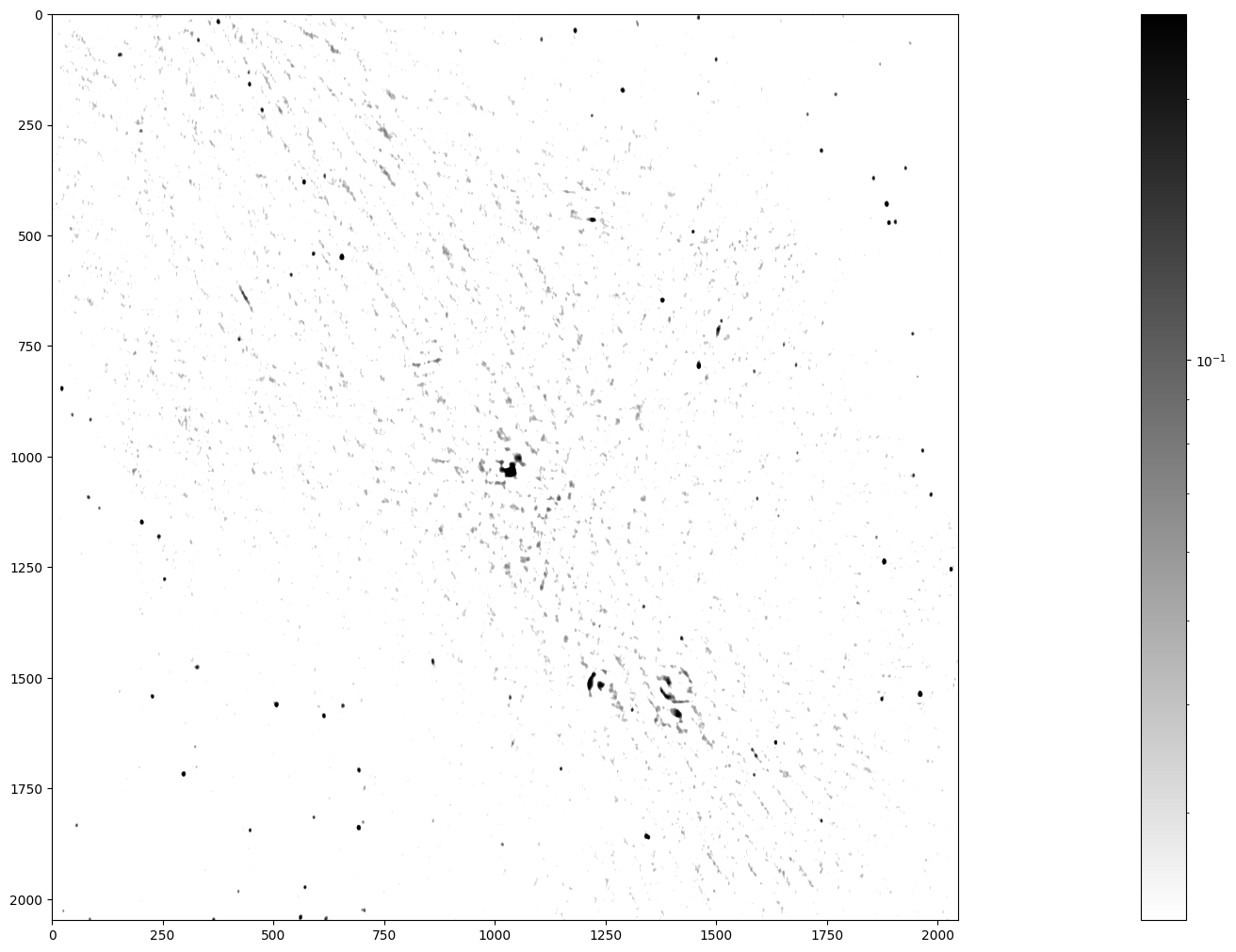
Image of the Galactic Center at the radio
frequency of 150 MHz
Accelerate your Python code with NumbaUsing Numba to execute Python code on the GPU
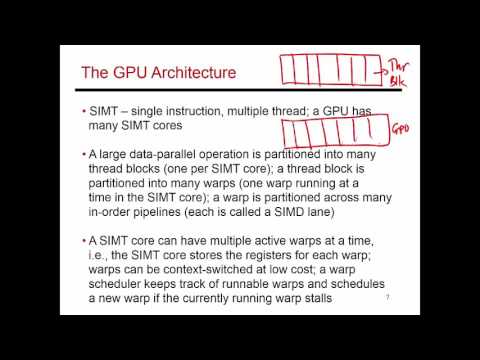
A Better Look at the GPUThe GPU, a High Level View at the HardwareHow Programs are ExecutedDifferent MemoriesAdditional Material
Figure 1

The connection between CPU and GPU
Figure 2