Introduction
Last updated on 2025-09-15 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 15 minutes
Overview
Questions
- What is green HPC system use and how can we approach it?
- What research activities produce carbon emissions?
Objectives
- Define green HPC system use.
- Appreciate emissions from HPC in the wider context of other research activities.
What is green HPC system use?
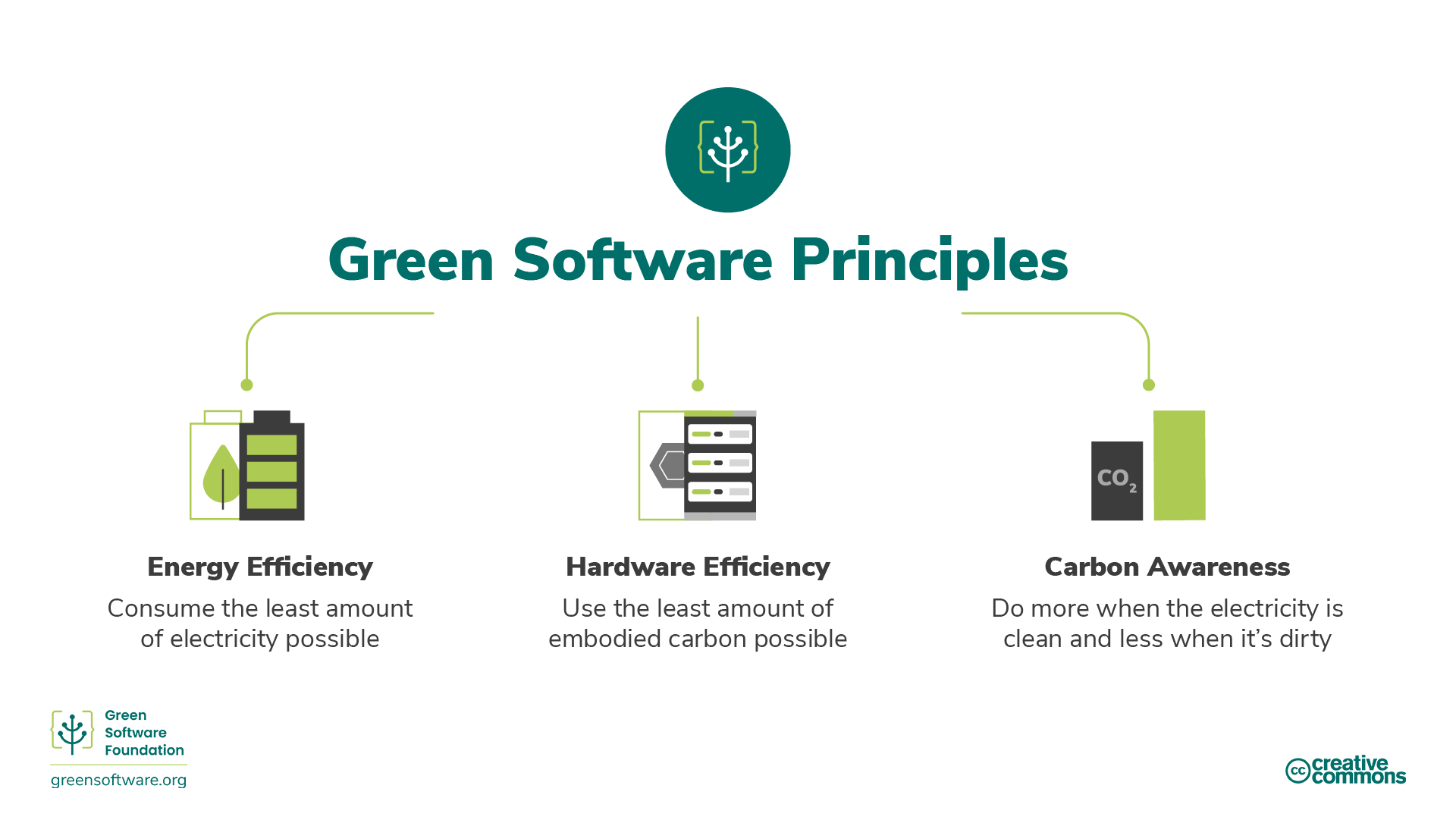
Green HPC system use is carbon-efficient HPC system use, meaning it emits the least carbon possible. Only three activities reduce the carbon emissions associated with HPC system use: energy efficiency, carbon awareness, and hardware efficiency.
This workshop will explain all of these concepts, how to apply them to use cases on high-performance computing (HPC) systems and how to measure them, as well as some of the international guidelines and organisations that guide and monitor this space.
How to understand green HPC system use
In this workshop, we cover the covers 6 key areas of green use of HPC systems (based on the principles of green software engineering):
- Carbon Efficiency: Emit the least amount of carbon possible.
- Energy Efficiency: Use the least amount of energy possible.
- Carbon Awareness: Do more when the electricity is cleaner and do less when the electricity is dirtier.
- Hardware Efficiency: Use the least amount of embodied carbon possible.
- Measurement: What you cannot measure, you cannot improve.
- Reducing Emissions: Understand mechanisms of carbon reduction.
Each of these episodes will introduce some new concepts and explain in detail why they are important in terms of the climate, and how you can apply them on HPC systems. We will use the ARCHER2 UK National Supercomputing Serivce to provide concrete examples of how the principles can be applied.
Other work activities
Use of HPC will be only one part of your activities associated with your work and may not even be the largest source of carbon emissions (though this does not mean you should not work to make your use of HPC more carbon efficient!). As well as understanding carbon emissions from HPC, which this workshop will help you do, you also need to assess other activities you undertake as part of your work and try to estimate emissions associated with them.
Exercise: What does your work look like?
Write down the activities that you do as part of your work or research that could be a source of carbon emissions other than from HPC systems. Once you have them written down, can you rank them in order of what you think the largest source of emissions will be to the smallest?
You may have come up with activities from the following list:
- Travel to/from place of work
- Travel to/from and accommodation at conferences, training and meetings
- Use of other computing resources (e.g. laptops/workstations, cloud resources and the internet)
- Data storage
- Laboratory work - chemicals, instruments
- Printed materials - books, journal articles
Ranking them in order is more difficult and will differ from person to person. Typically, any sort of flying to conferences or meetings will be the most carbon intensive activity you can undertake through your work. Whether it is the largest contribution depends on how often you fly. If you work in a laboratory, that may well be the next highest source of emissions though if you commute a long way and use a petrol/diesel car that may also be one of the highest sources of emissions.
In fact, all activities that we undertake as part of our work (and personal life) produce carbon emissions. While, in an ideal world, we would be able to reduce emissions from all our activities we have finite time and effort so need to prioritise based on which reduction strategies will have the largest impact. This means that the first step is to estimate the emissions from different activities we are involved in as part of our work, even if the estimate is very rough. The links below can help to calculate your emissions:
- Travel emissions calculator (Deloitte UK)
- Emissions from laptops (Circular Computing)
- Transparent reporting of research-related greenhouse gas emissions through the scientific CO2nduct initiative
- Quantifying the carbon footprint of clinical trials: guidance development and case studies
- Emissions measurement and reporting approaches for the public sector (UK Government)
- Carbon footprint and mitigation strategies of three chemistry laboratories
- This course covers green HPC system use, in particular:
- Carbon Efficiency: Emit the least amount of carbon possible.
- Energy Efficiency: Use the least amount of energy possible.
- Carbon Awareness: Do more when the electricity is cleaner and do less when the electricity is dirtier.
- Hardware Efficiency: Use the least amount of embodied carbon possible.
- Measurement: What you cannot measure, you cannot improve.
- Reducing Emissions: Understand mechanisms of carbon reduction.
