Summary and Schedule
This lesson introduces environmental sustainability principles in the context of high performance computing (HPC) systems. Understanding the scale of emissions from different sources is critical to being able to make changes to work in a more environmentally sustainable way. This lesson will give you the ability to understand emissions arising from use of HPC systems and how to quantify them. We will use practical examples and real data from an existing HPC facility to illustrate the concepts.
We use the UK National Supercomputing Service, ARCHER2 as an example throughout this lesson but the principles and learning should be applicable to any HPC system.
After completing this lesson you should:
- Be able to understand the concept of carbon efficiency and how it relates to energy efficiency - including cases where energy efficiency can be at odds with carbon efficiency
- Know about how HPC systems potentially reduce emissions
- Understand carbon intensity of electricity generation and the implications for carbon aware use of HPC
- Appreciate the embodied emissions associated with HPC hardware and how they impact carbon aware use of HPC
- Be aware of the frameworks used to measure and report on carbon emissions and how the terms used in these frameworks map onto HPC
- Gain practical advice on how you can measure and improve the carbon efficiency of your use of HPC
This workshop is based on and builds on the material in the Green Software Practitioner course developed by the Green Software Foundation.
Target audience
Anyone involved in using or delivering HPC resources - a user, a developer of software for use on HPC, an HPC service operator, or those involved in procuring HPC systems. By attending this course, you will be able to better understand the effect of HPC systems on carbon emissions, where it fits with emissions from other activities, and what concrete actions can be taken to reduce emissions and the size of the impact from these reductions. No knowledge of environmental sustainability principles is assumed.
Prerequisites
Attendees should familiarise themselves with the key concepts below before attending the workshop.
| Setup Instructions | Download files required for the lesson | |
| Duration: 00h 00m | 1. Introduction |
What is green HPC system use and how can we approach it? What research activities produce carbon emissions? |
| Duration: 00h 15m | 2. Carbon Efficiency |
What does the term carbon equivalence (CO2e) mean? Can we also have positive emissions impacts from HPC systems? |
| Duration: 00h 35m | 3. Energy Efficiency |
What are low carbon sources of electricity generation? How do we quantify energy efficiency? What aspects should we consider when looking at energy efficiency of HPC system use? |
| Duration: 01h 05m | 4. Carbon Awareness |
How does electricity generation affect GHG emissions? What is carbon intensity of electricity generation and how does it vary geographically and temporally? What techniques can I use to make my use of HPC greener and influence transition to low-carbon electricity generation? |
| Duration: 01h 40m | 5. Hardware Efficiency |
What is embodied carbon on HPC systems? How can embodied carbon efficiency be improved on HPC systems? What can I do to improve the embodied carbon efficiency during my use of HPC systems? |
| Duration: 02h 00m | 6. Measurement |
How are emissions measured and classified under the GHG
protocol? How do I use the GHG protocol to estimate emissions from my use of HPC? |
| Duration: 03h 00m | 7. Reducing Emissions |
What methodologies are available to reduce carbon emissions and how do
they differ? What is the difference between “net zero” and “carbon neutral” climate commitments? How can I reduce the emissions from my use of HPC systems? |
| Duration: 03h 45m | 8. Next Steps | What other resources are available to help me be more environmentally sustainable? |
| Duration: 03h 55m | Finish |
The actual schedule may vary slightly depending on the topics and exercises chosen by the instructor.
Before attending the workshop you should spend a short amount of time familiarising yourself with the “Key concepts” described below.
The other section on Green Software Engineering is provided for interest (particularly if you are a software developer or are designing AI models). Reading this section is not required to participate in the course.
Key concepts
Global warming vs climate change
Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning. Climate change is long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may be natural, but since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change.
Climate vs weather
Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere in a short period of time. Climate refers to the conditions of the atmosphere over long periods of time. Any changes to the long-term condition of the atmosphere will also cause changes to the short-term conditions. Some examples of measurable changes to weather conditions due to climate change are:
- Changes to the water cycle, including rainfall
- Melting of ice
- Heating of the land, air, and ocean
- Changes in ocean currents, acidity, and salinity
These changes can lead to flooding - both in coastal areas and due to increased rainfall - drought, wildfires and more frequent extreme weather conditions.
Greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect
Greenhouse gases are a group of gases that trap heat from solar radiation in the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases act as a blanket, increasing the temperature on the surface of the Earth. This is a natural phenomenon which has been accelerated due to man-made carbon emissions. Now the global climate is changing at a faster rate than that at which animals and plants can adapt.
Greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect are crucial to all life on Earth and often come from natural sources like animals, volcanoes, and other geological activity. The greenhouse effect allows the Earth to maintain a higher temperature than it would without them by capturing more heat from solar radiation. Like many other natural processes of the Earth, the greenhouse effect is a balance that can be upset by multiple factors.
Monitoring climate change
As a result of the effects of climate change and an ever-increasing number of destructive weather events, efforts have been made by the global community to address these issues and take steps to control and limit global warming in order to mitigate and reverse the effects of climate change.
The Paris Climate Agreement is an international treaty agreed in 2015 by 196 parties and the UN to reduce the Earth’s temperature increase. The agreement is to keep the rise in global mean temperature to 2°C compared to pre-industrial levels, with a preferable lower limit of 1.5°C. The agreement is reviewed every five years and mobilizes finance to developing nations to mitigate the impacts of climate change and prepare for and adapt to the environmental effects caused by climate change. In addition, each party is expected to update its progress through a Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC). As of October 2024, 195 parties, including the UK, have joined the agreement.
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is a group created to achieve the stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous interference with the climate system.
The COP (Conference of the Parties) is an annual event involving all parties in the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. At the conference, each party member’s progress on tackling global warming, as agreed as part of the Paris Climate Agreement, is reviewed and assessed. The COP is also a chance for parties to come together and make decisions that will reduce the effects of global warming. Common topics include strategies to reduce carbon, financing low carbon strategies and preservation of natural habitats.
The IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), created by the UN in 1988, aims to provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies. IPCC reports are also a key input into international climate change negotiations. The IPCC is an organization of governments that are members of the United Nations or the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The IPCC currently has 195 members.
We will always emit carbon through our activities, but being carbon efficient means minimising the amount of carbon emitted per unit of work. We aim to ensure that for each gram of carbon we emit into the atmosphere, we extract the most value possible.

History of green software engineering
In 2019 the original eight principles of green software engineering were released. The 2022 update of the principles took on feedback received over the years, merging some principles and adding a new one regarding understanding climate commitments. The principles as they are written are aimed primarily at software engineers but they are more broadly applicable to anyone making use of digital infrastructure. In this lesson we specifically look at how they can be applied to use of HPC resources. The principles are:
- Carbon Efficiency: Emit the least amount of carbon possible.
- Energy Efficiency: Use the least amount of energy possible.
- Carbon Awareness: Do more when the electricity is cleaner and do less when the electricity is dirtier.
- Hardware Efficiency: Use the least amount of embodied carbon possible.
- Measurement: What you cannot measure, you cannot improve.
- Climate Commitments: Understand the exact mechanism of carbon reduction.
These principles were originally described by the Green Software Foundation.
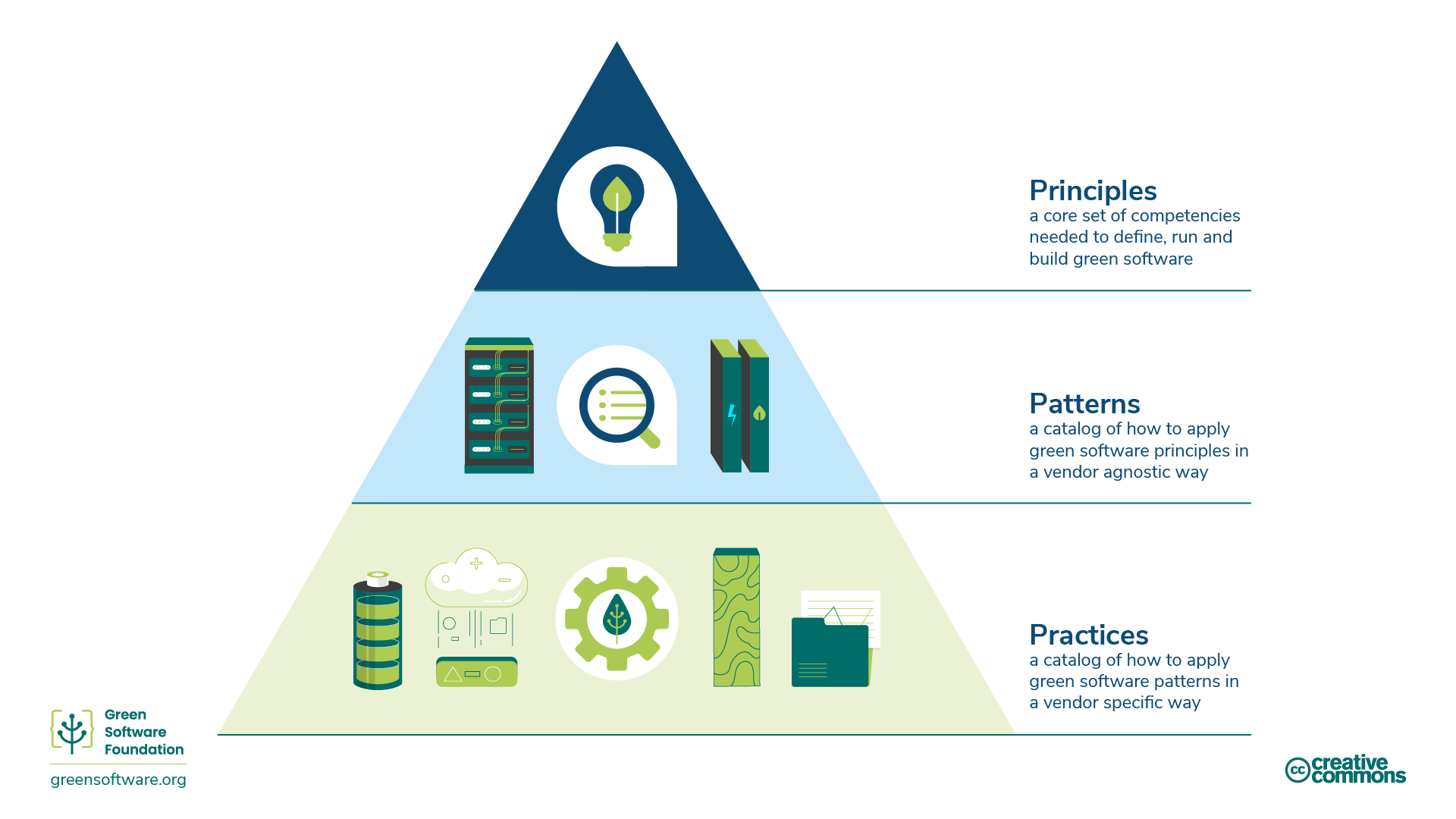
Principles, Patterns, and Practices.
Above, we described the principles of green software, a core set of competencies needed to define, build and run green software. To support software engineers in this area, The Green Software Foundation has developed a catalogue of green software patterns. While not specific to use of HPC and aimed at software developers rather than users, they provide interesting information on how particular software types and their use can be made more environmentally sustainable.
A green software pattern is a specific example of how to apply one or more principles in a real-world example. Whereas principles describe the theory that underpins green software, patterns are the practical advice software practitioners can use in their software applications today. Patterns are vendor-neutral.
A green software practice is a pattern applied to a specific vendor’s product and informs practitioners about how to use that product in a more sustainable way.
Practices should refer to patterns that should refer to principles.
The green software foundation publishes a catalog of vendor-neutral green software patterns across various categories.