An Introduction to the Internet of Things
Figure 1
Computers connected to form a Local Area
Network
Figure 2
When two networks are connected they form an
internet. These networks can connect to the worldwide internet known as
The Internet.
Figure 3
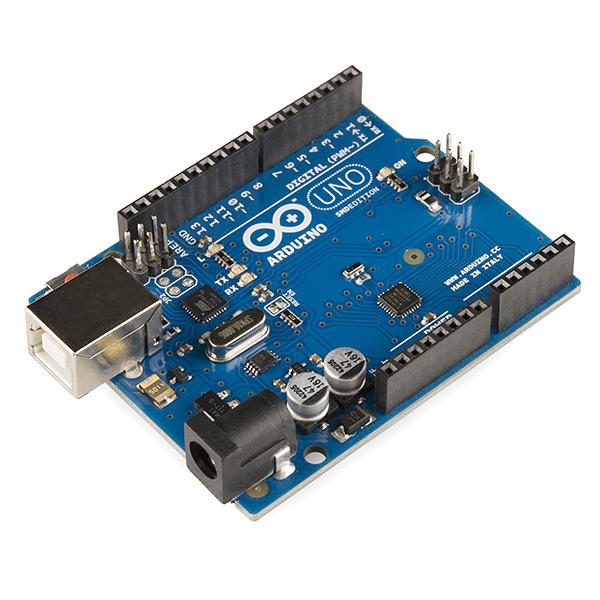
The original and most basic Arduino - the
Arduino Uno
Figure 4
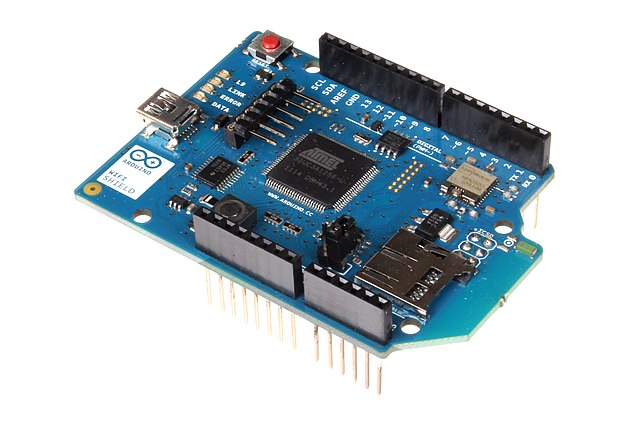
A WiFi shield for the Arduino Uno
Figure 5
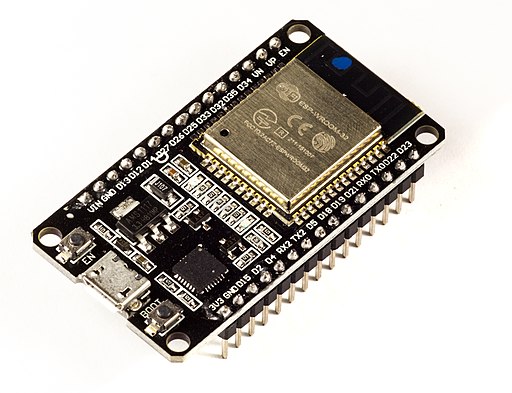
An ESP32 WROOM 32
The Arduino IDE
Figure 1

Arduino Splash Window
Figure 2
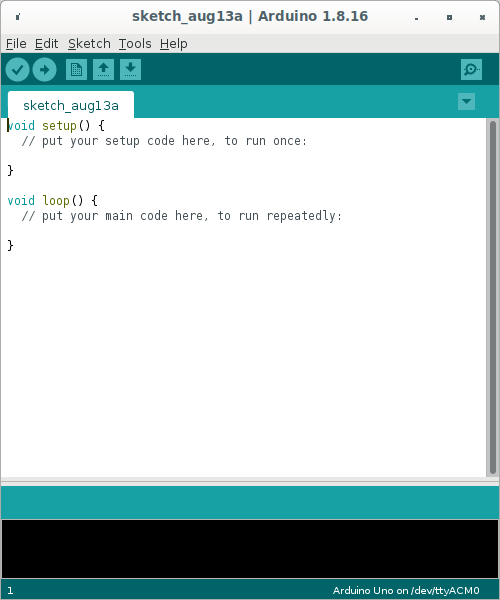
Arduino IDE
Figure 3
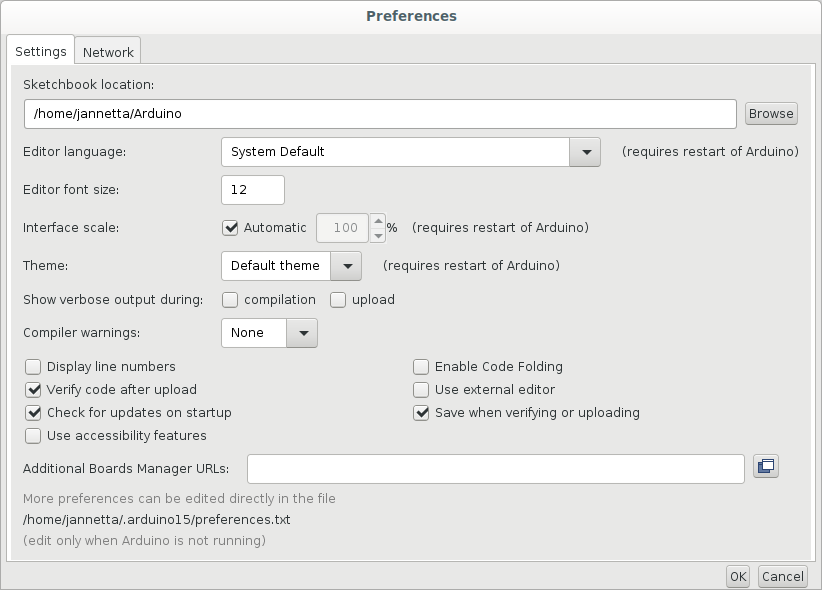
Preferences Window
Figure 4
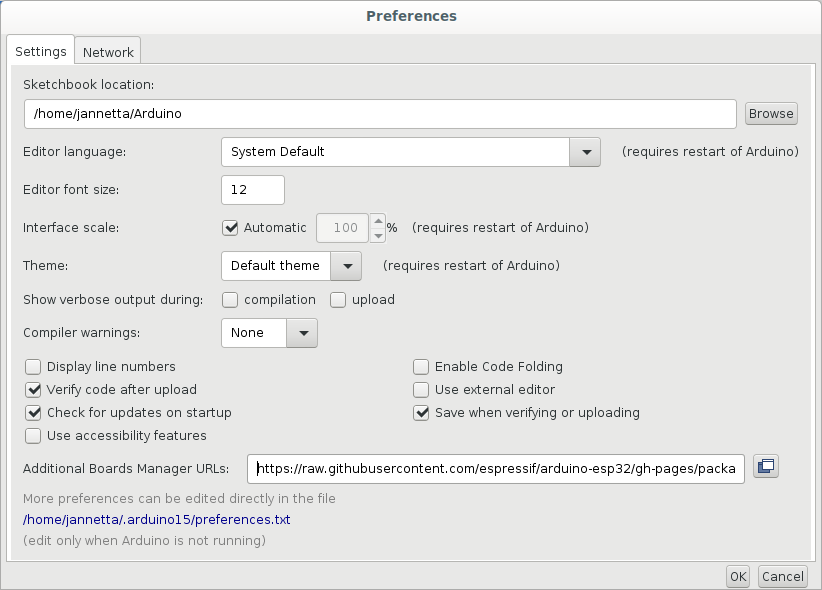
Enter additional boards manager URLs
Figure 5
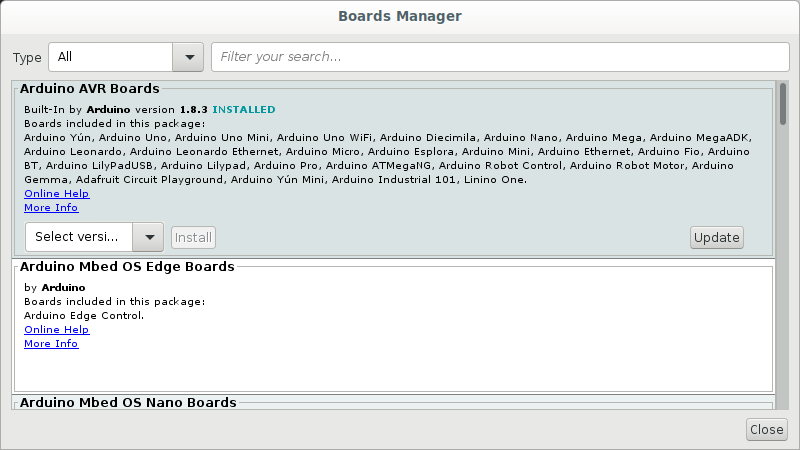
Boards Manager
Figure 6
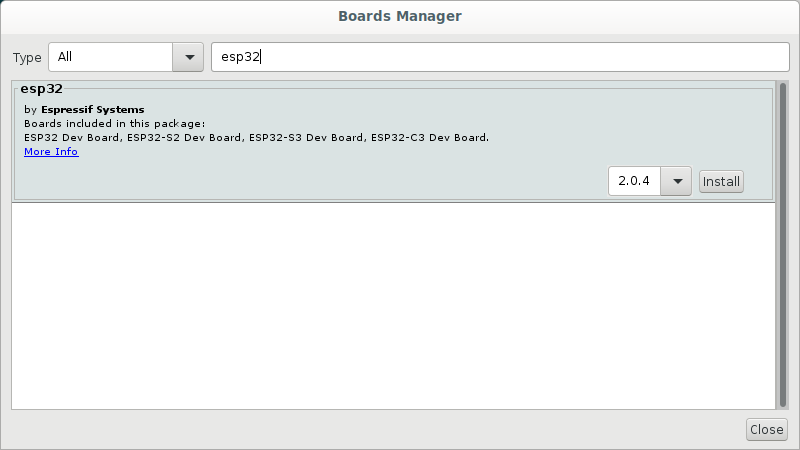
Select esp32 and Install
Figure 7
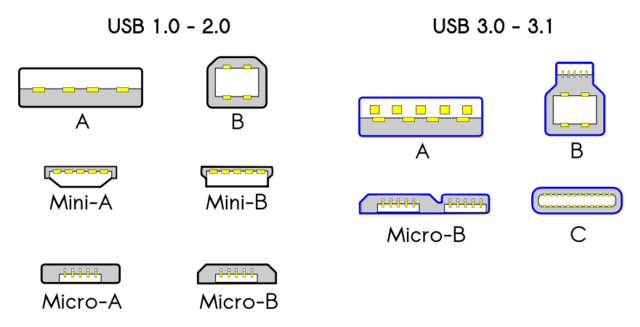
USB connectors
Figure 8
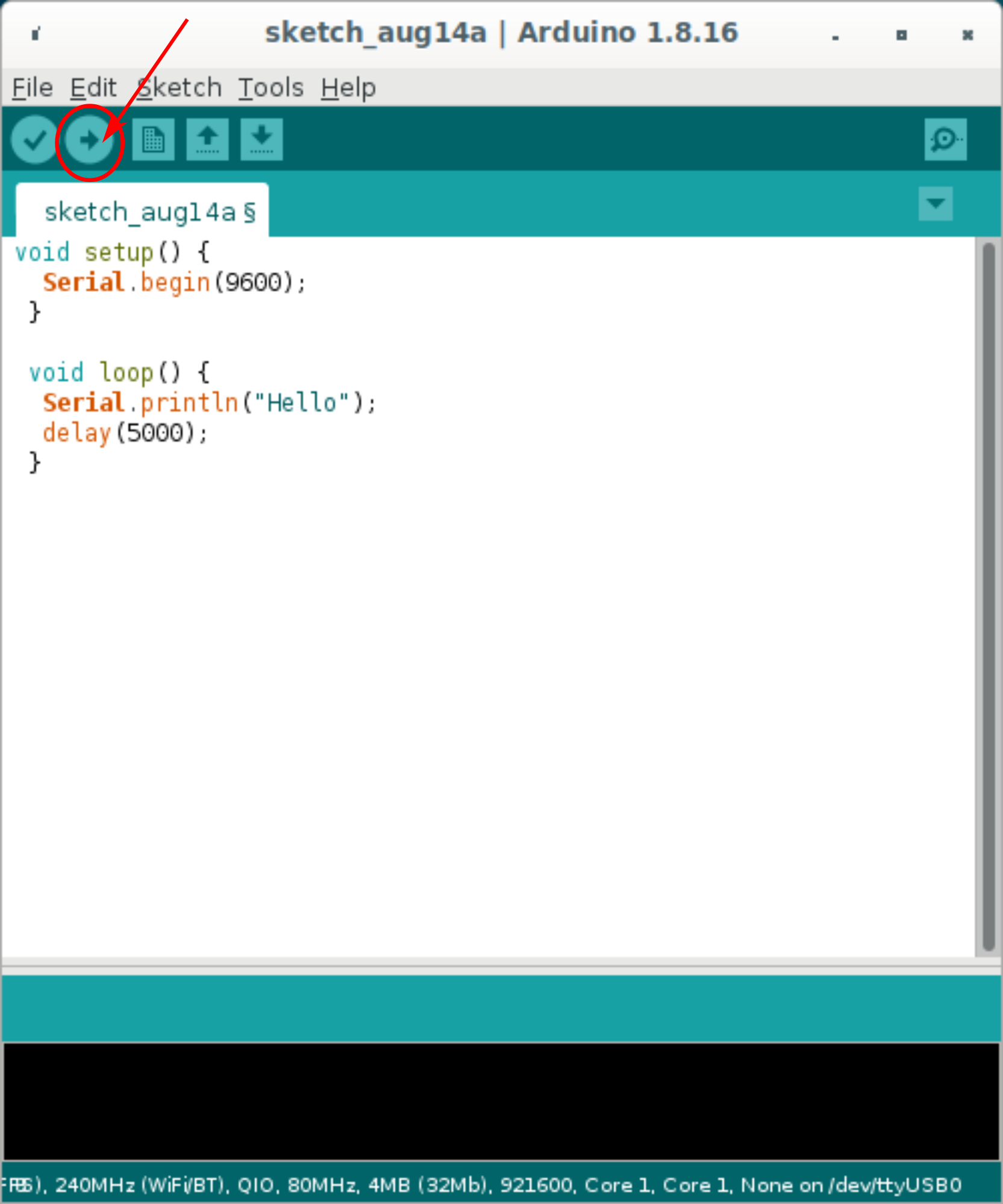
Click the
compile and run
buttonFigure 9
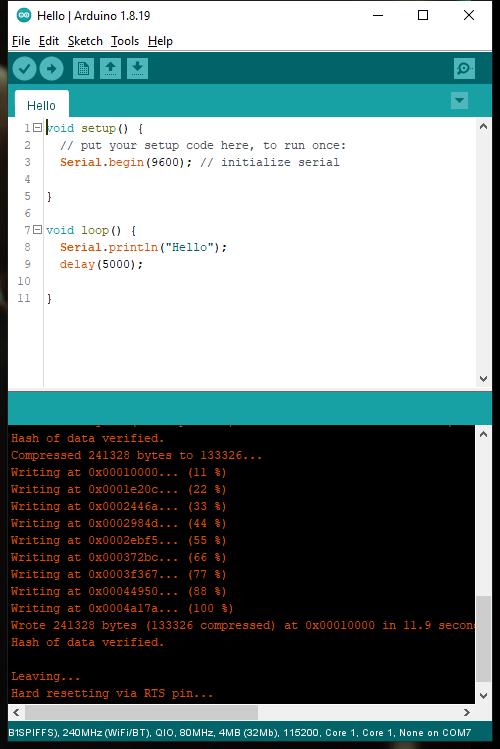
Code compiled and uploaded
Figure 10
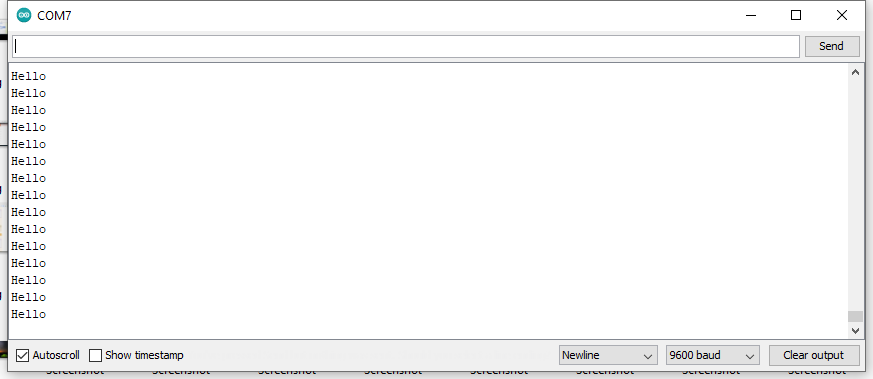
Serial Monitor
Understanding the code
Connecting the first sensor
Figure 1
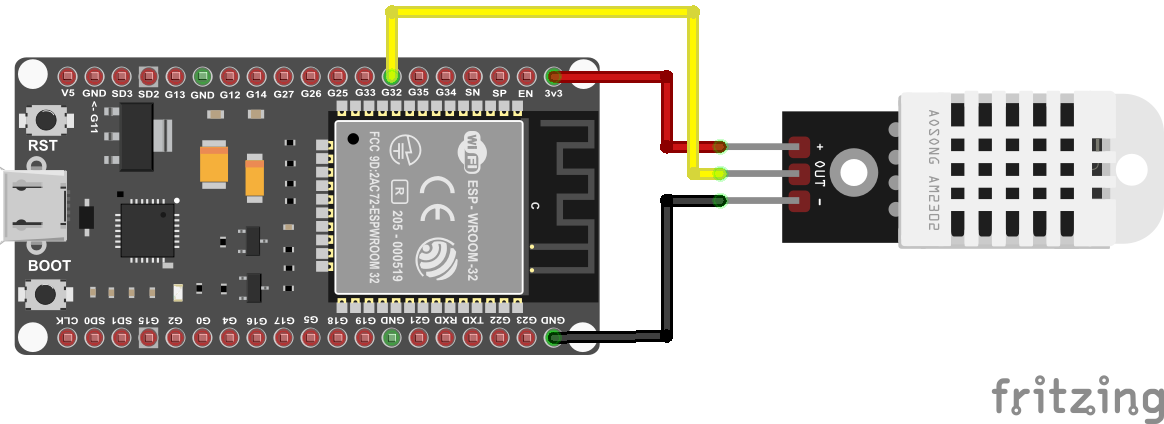
Temperature Sensor module (DHT22)
Figure 2
Wiring the DHT11 Temperature Sensor when it is
not part of a module
Figure 3
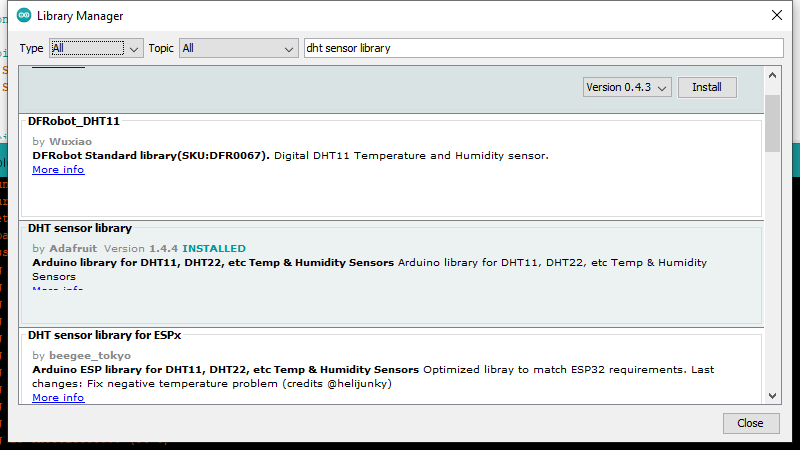
Library Manager
Connecting the second sensor
Figure 1
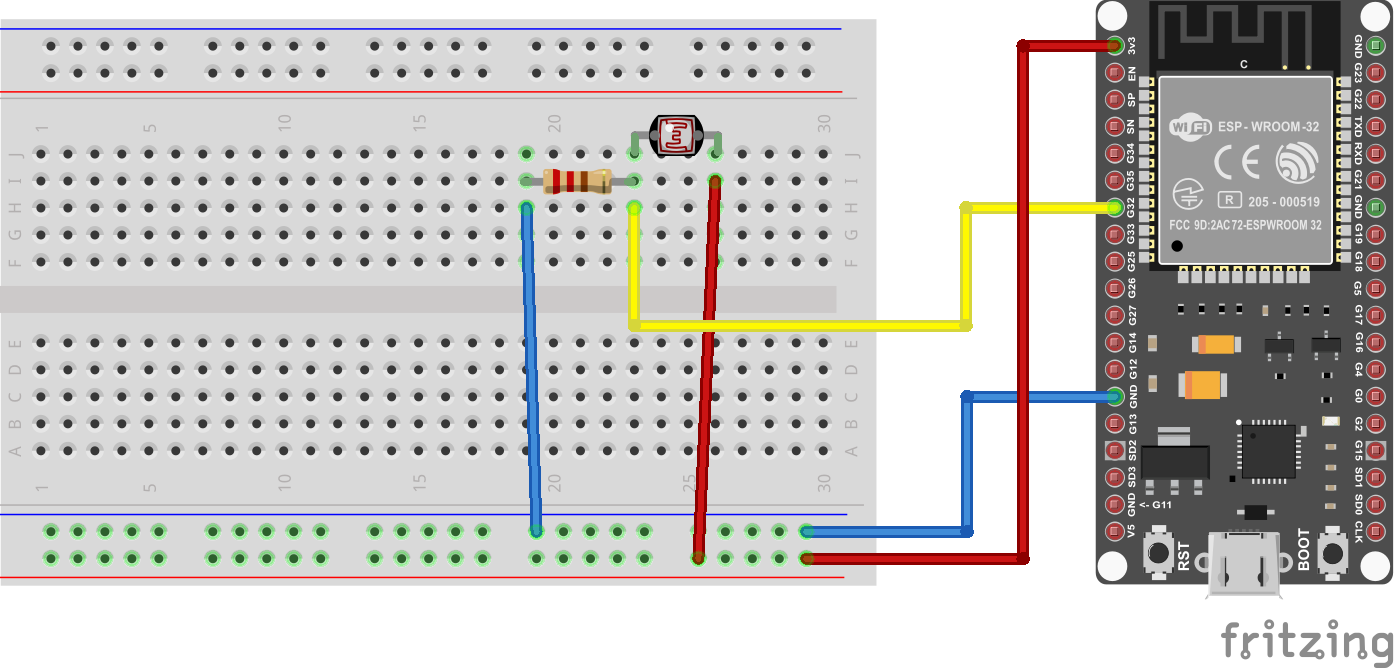
Light Level with a Light Dependent Resistor
(LDR)
Combining the two circuits
Figure 1
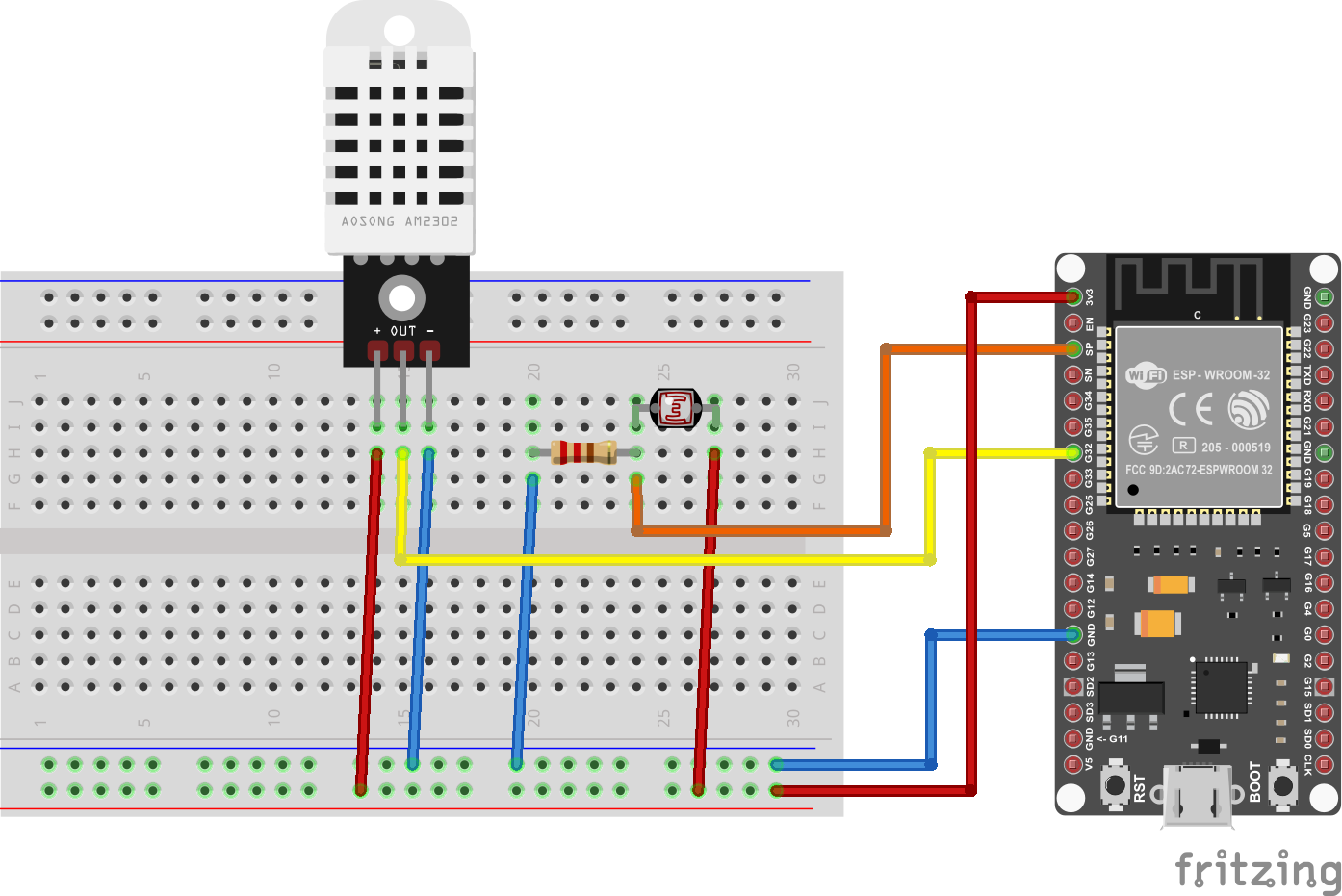
Circuit with the DHT22 temperature sensor and
and LDR light for measuring light intensity
Using MQTT for the Internet of Things
Figure 1
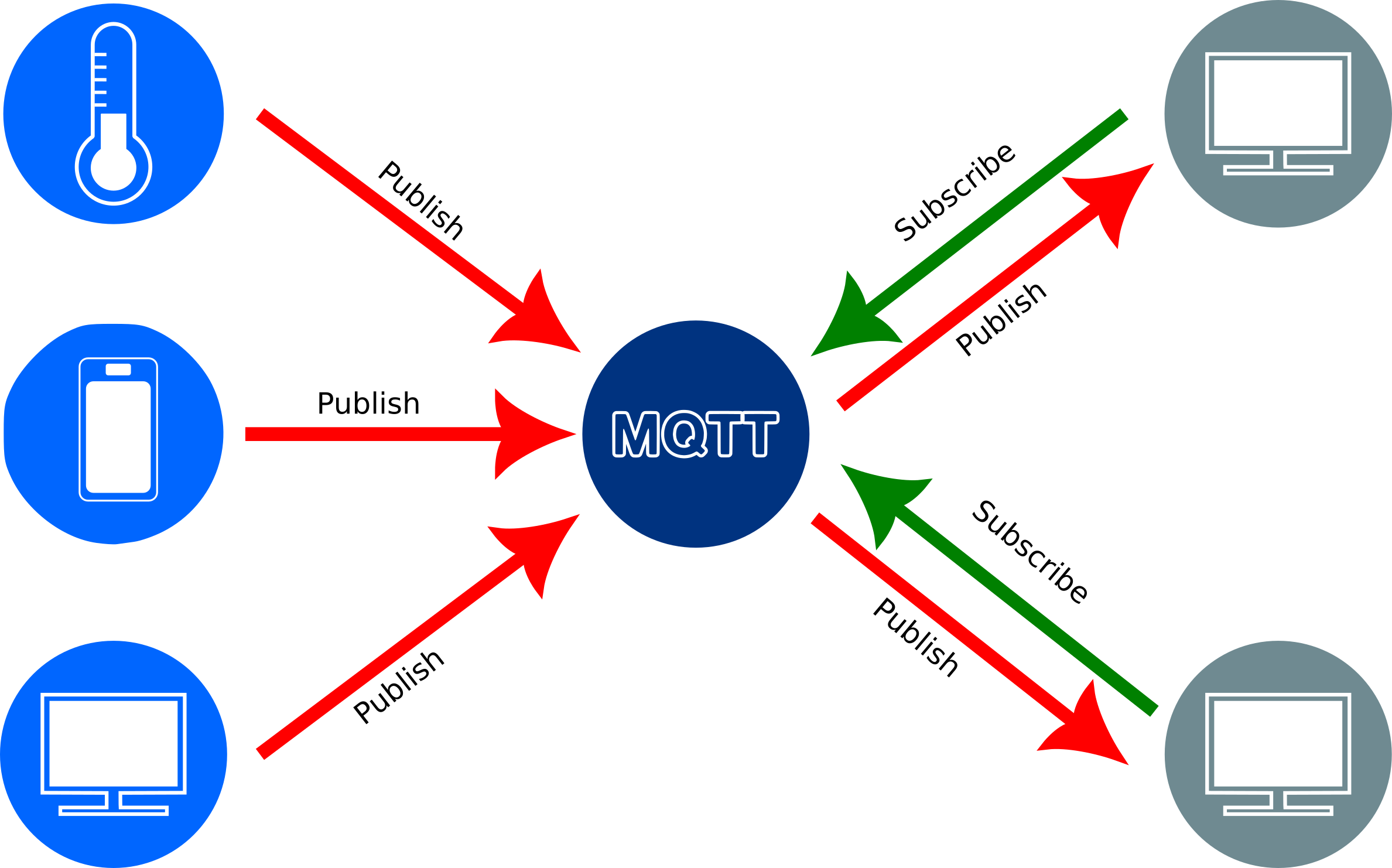
MQTT Architecture
Figure 2
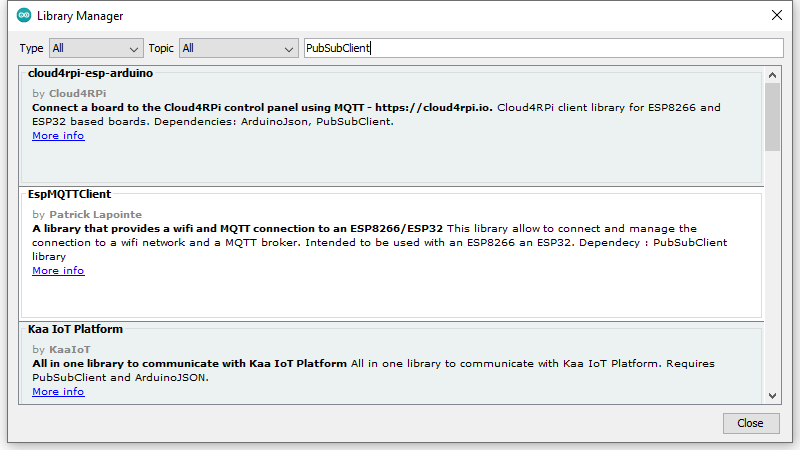
Installing the PubSubClient library for MQTT
messaging
Figure 3
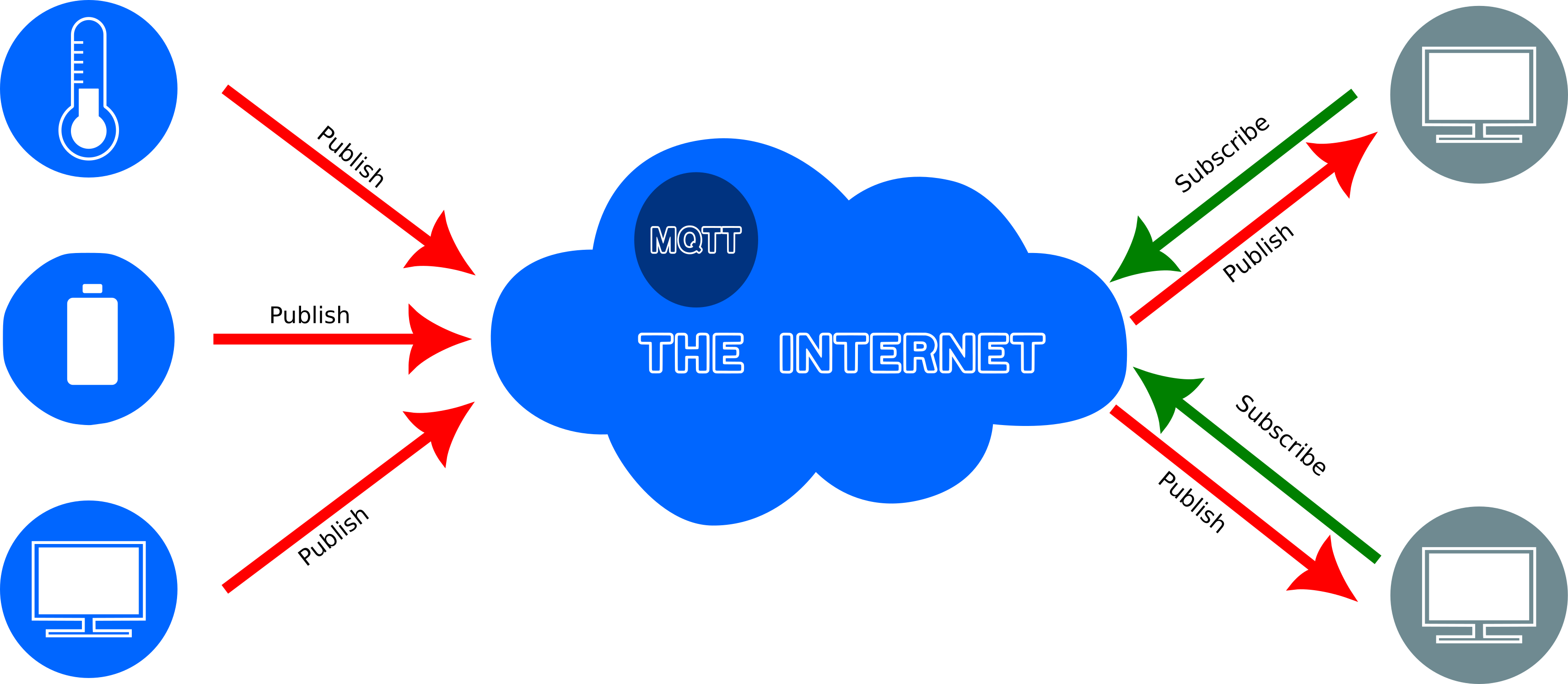
An MQTT broker on the Internet
Figure 4
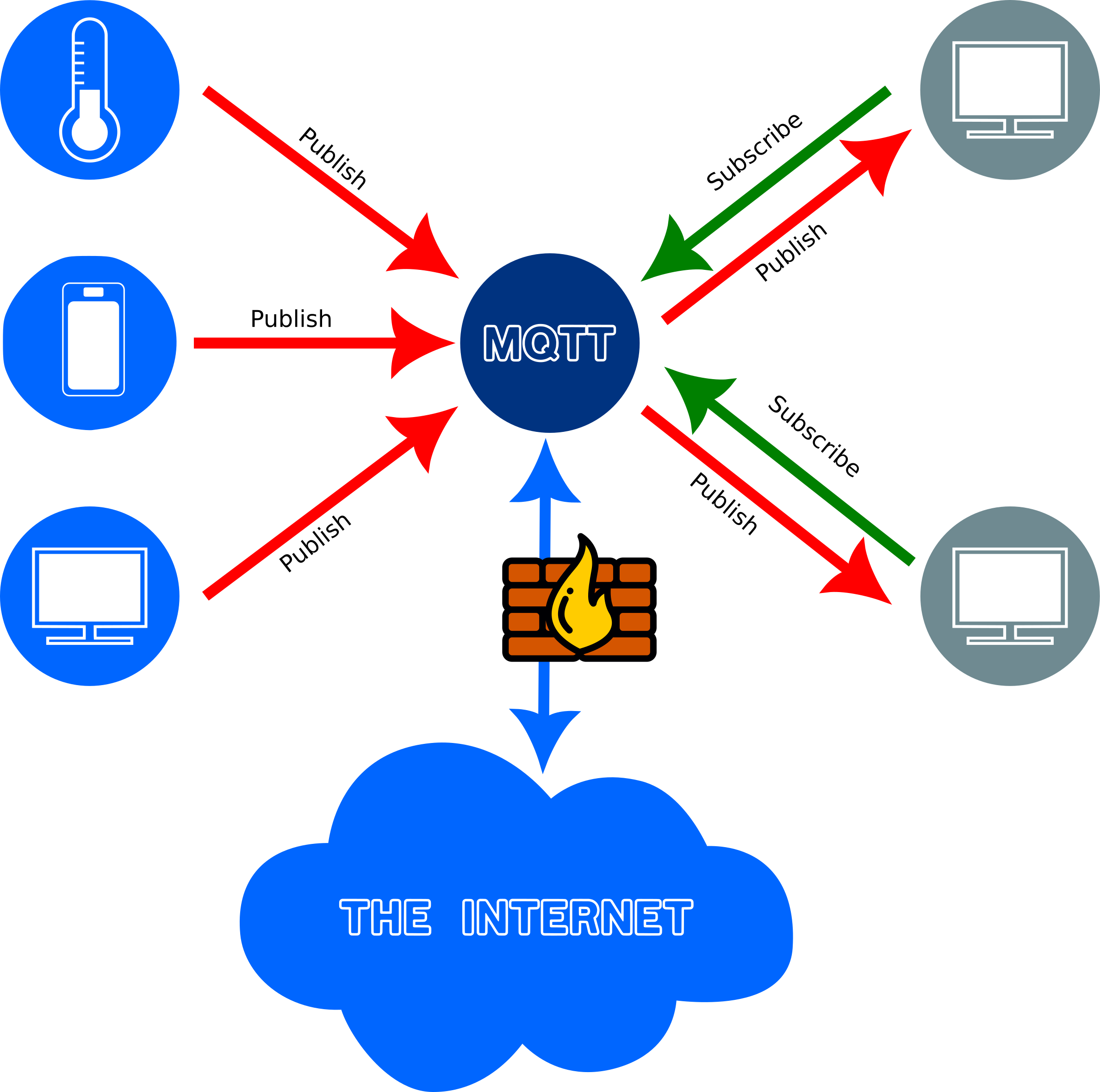
An MQTT broker on a private network
Subscribing to an MQTT topic
Figure 1
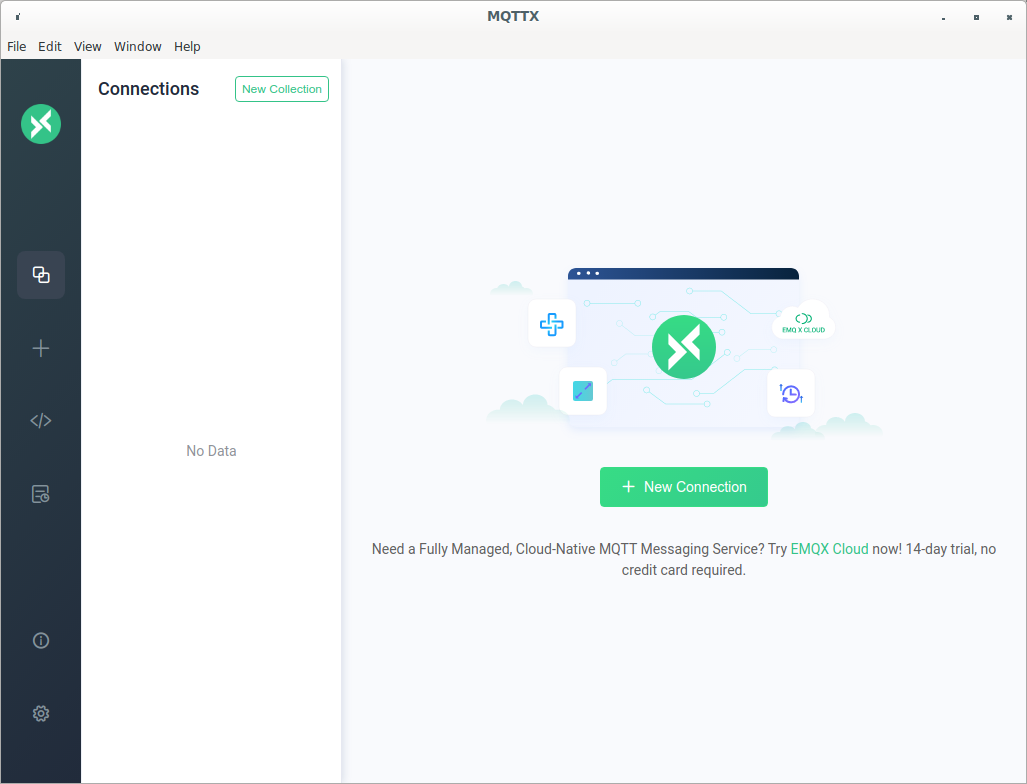
Running MQTTX
Figure 2
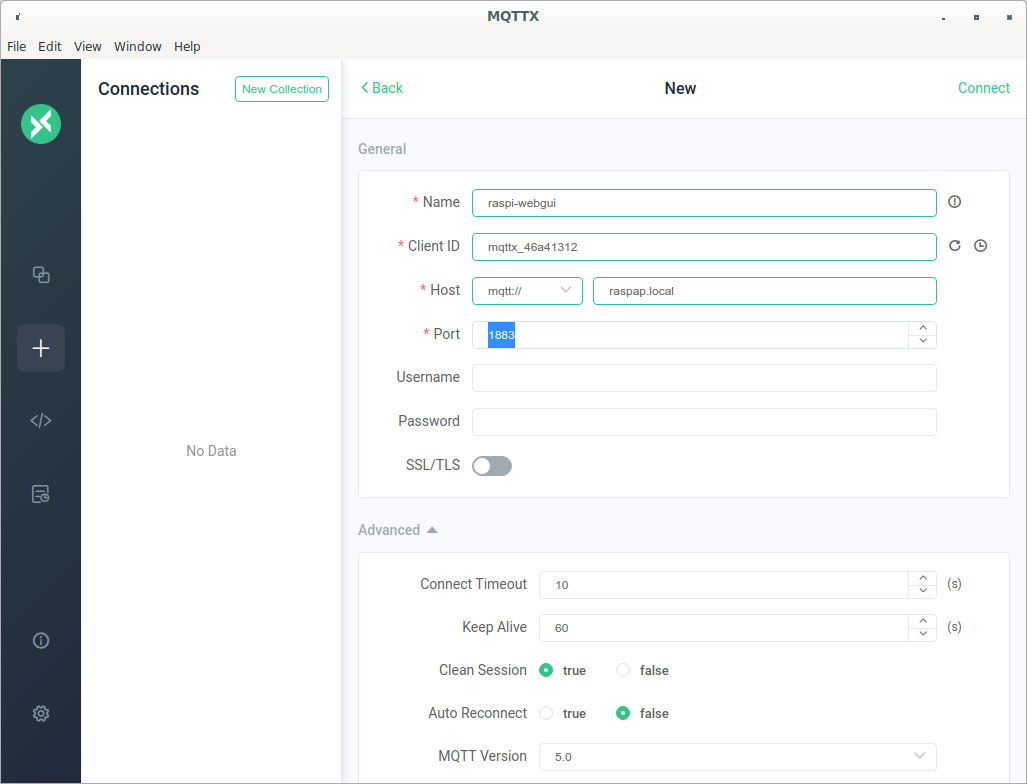
New connection in MQTTX
Figure 3
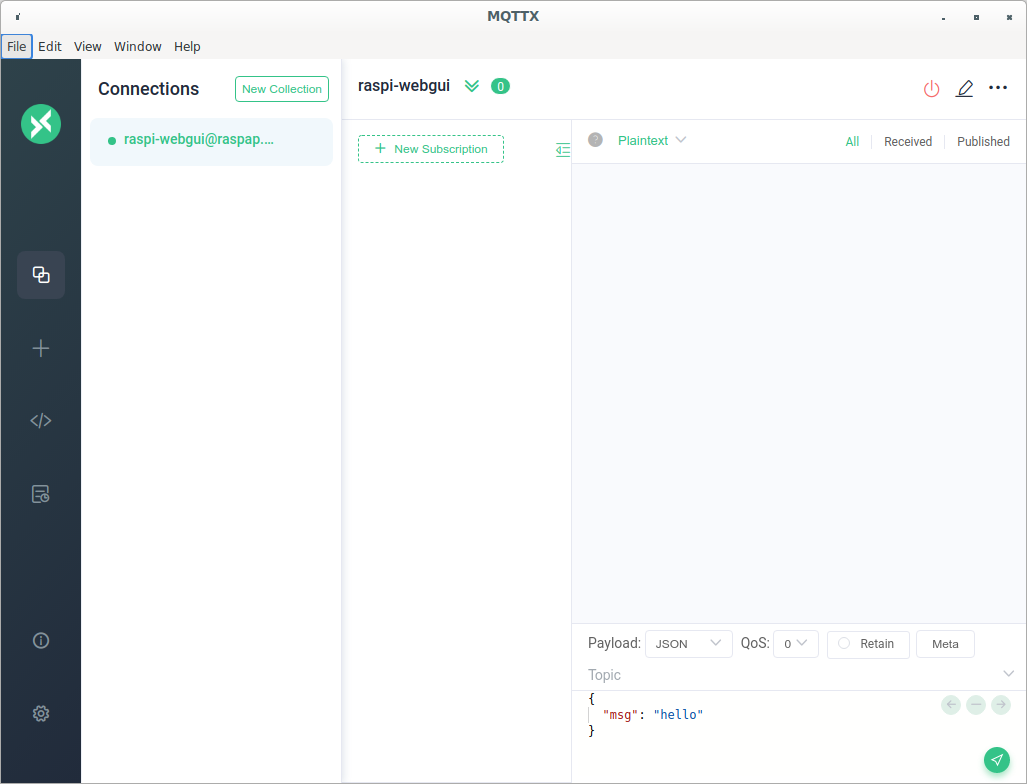
MQTTX connected to broker
Figure 4
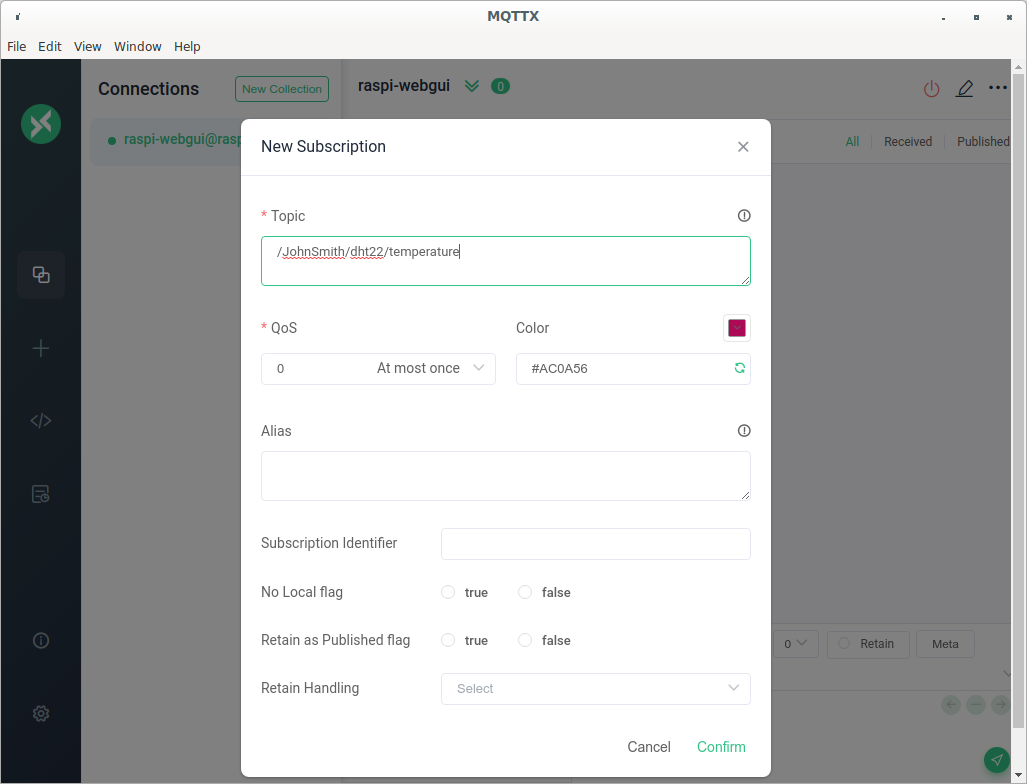
New Subscription
Figure 5
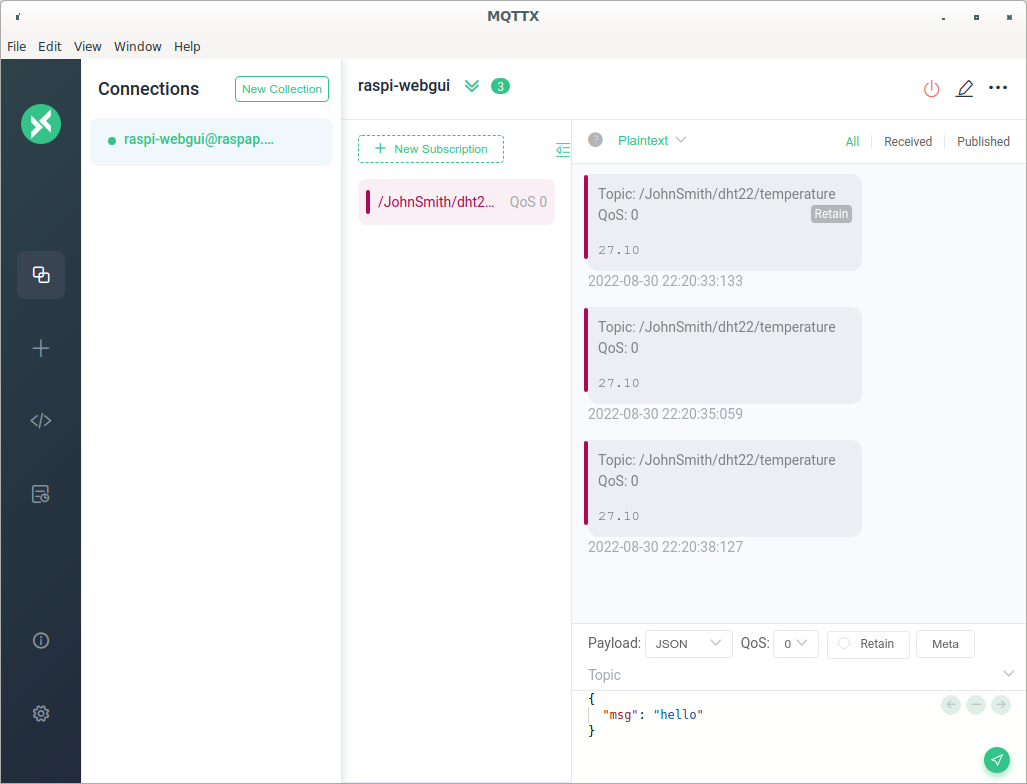
Subscribed
