sMRI Quality Control
Last updated on 2025-02-26 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 30 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do we identify image preprocessing failures?
Objectives
- Visualize processing failures
- Familiarize with automatic QC tools
You Are Here!
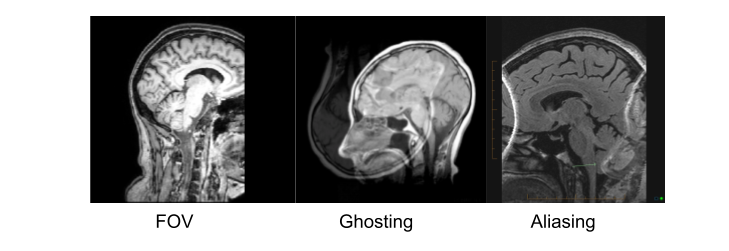
Things that can go wrong…
Acquistion
Quantification
Exisiting image processing pipelines (e.g. FreeSurfer, CIVET) will have a few QC tools and examples that can help with failure detection and quality control of volumetric segmentations and surface parcellations.
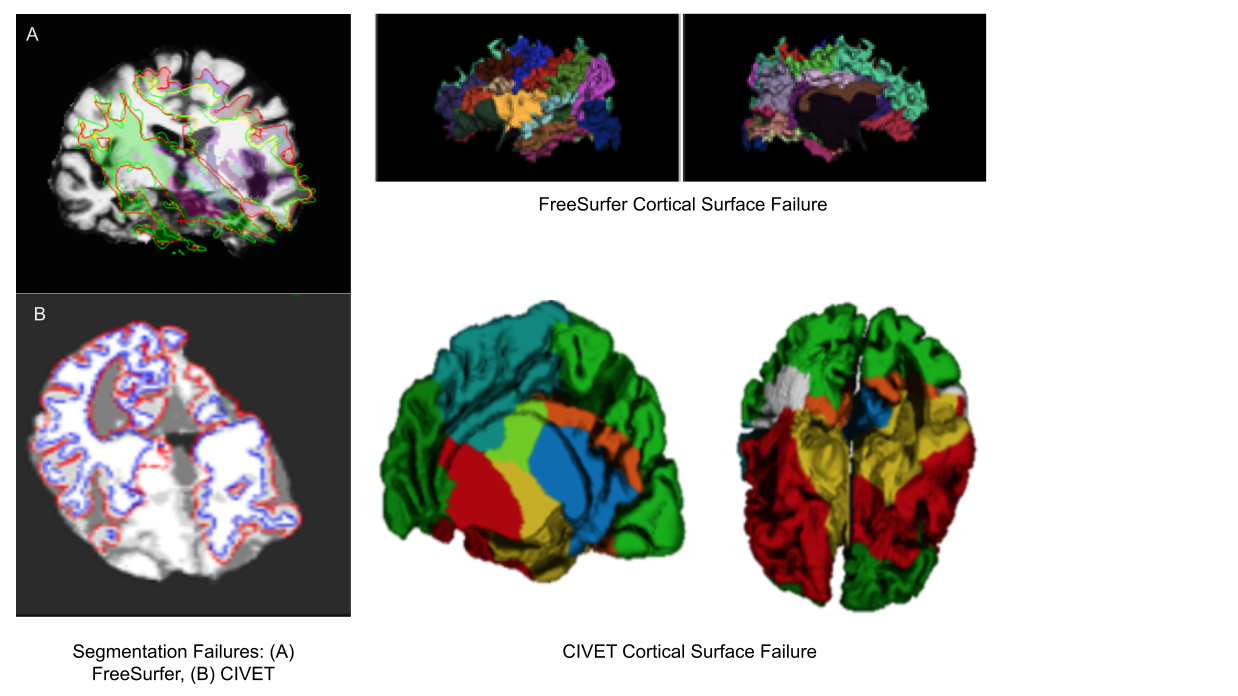
Usage of new method will require your own QC protocols. Especially for highly specific segmentation methods require visual inspection from a neuroanatomy expert. Even for the qualitiative visual inspection, it is important create a QC protocol and share it with the results.
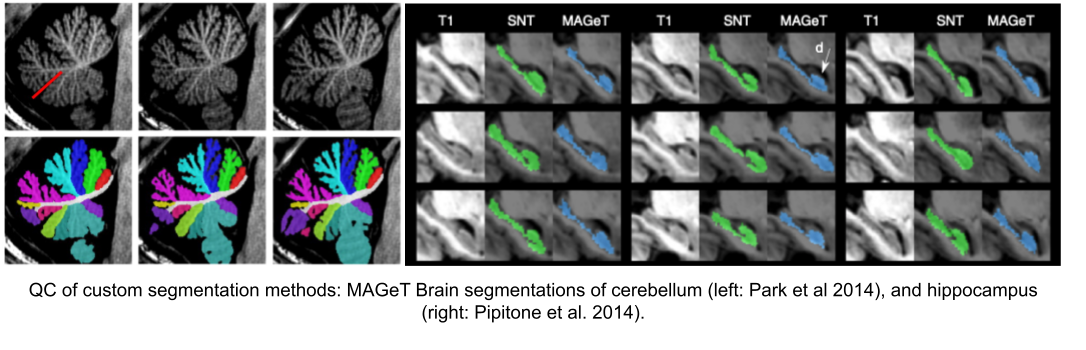
Note: see Hippocampal and cerebellar for segmentation method details.
Automatic QC tools
Using reports from exisiting pipelines: https://fmriprep.org/en/stable/_static/sample_report.html
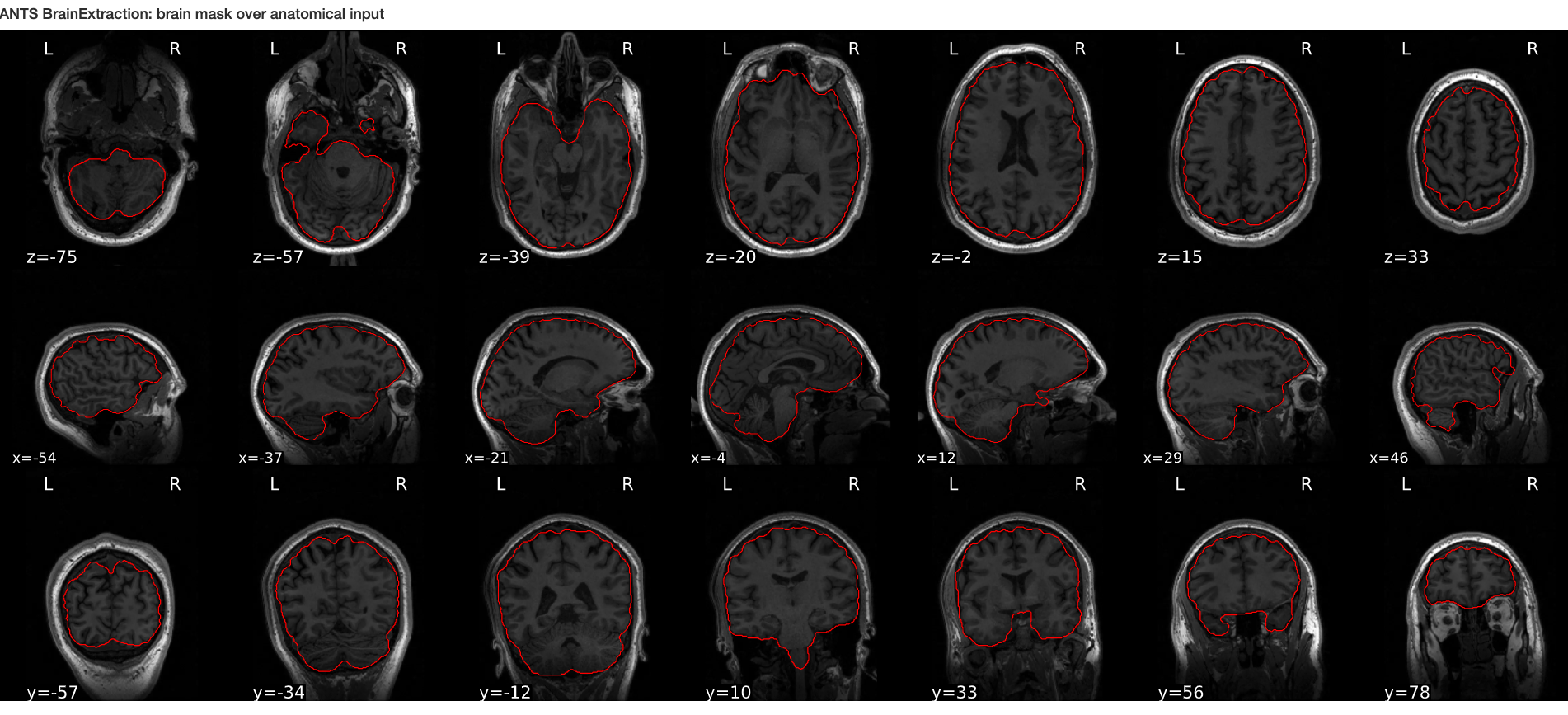
Using QC tools
MRIQC: extracts no-reference IQMs (image quality metrics) from structural (T1w and T2w) and functional MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) data. (Developed by the Poldrack Lab at Stanford University for use at the Center for Reproducible Neuroscience (CRN), as well as for open-source software distribution.)
| Individual report | Group report |
|---|---|
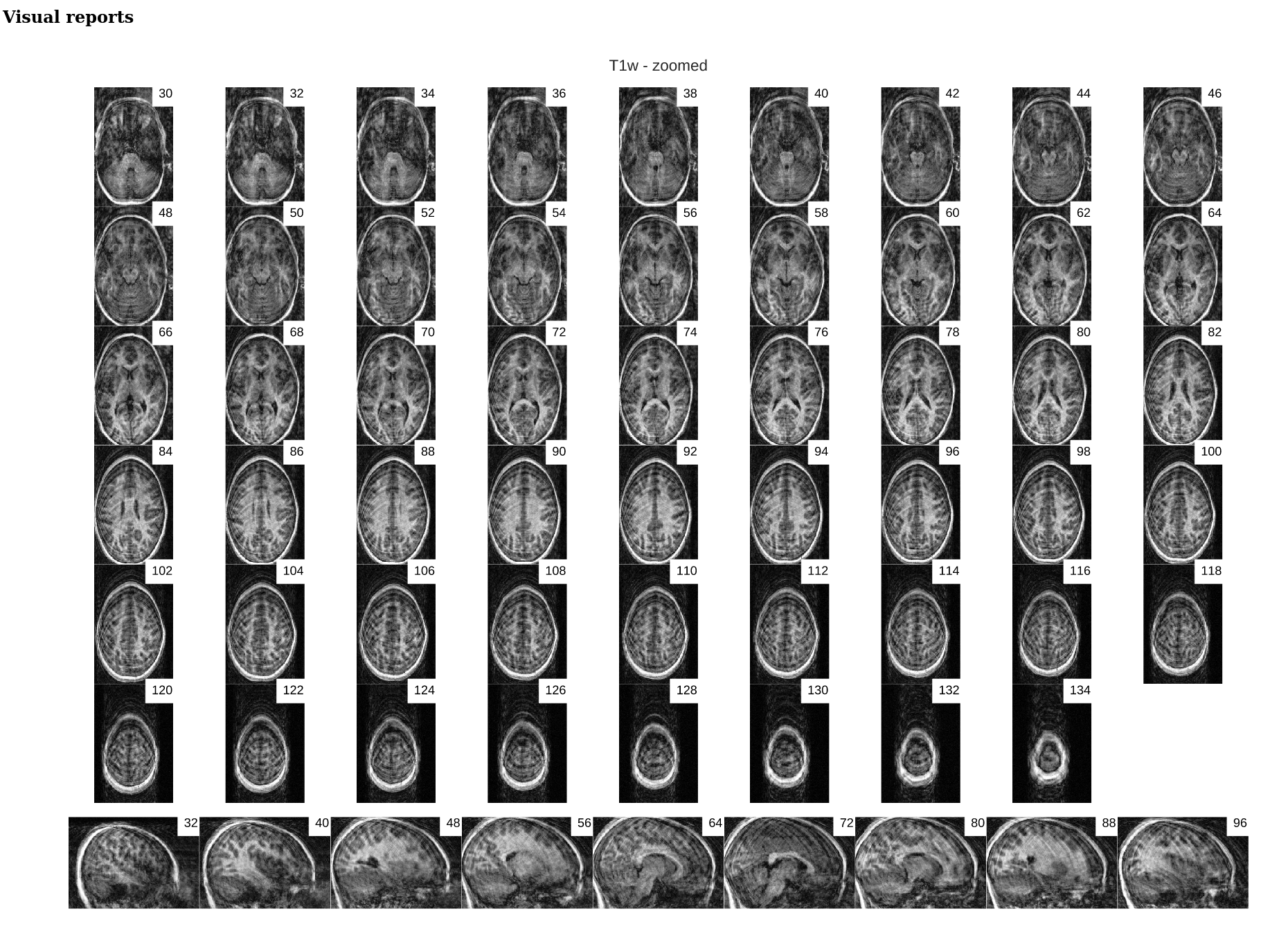 |
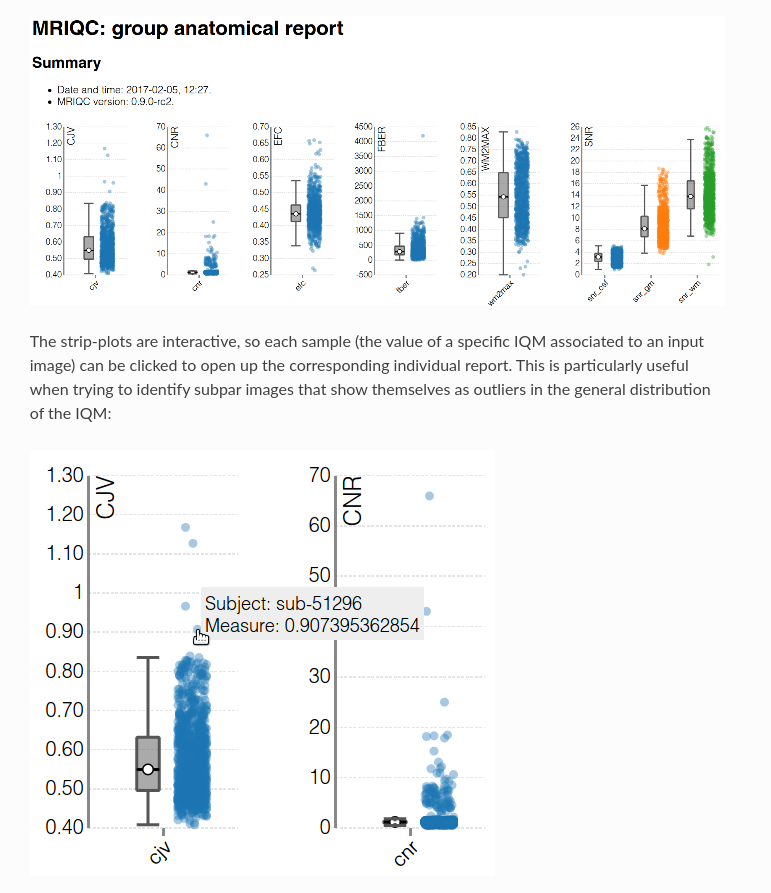 |
VisualQC: assistive tool to improve the quality control workflow of neuroimaging data (Author: Pradeep Reddy Raamana).
| T1w acquisition | Alignment | Cortical Parcellation |
|---|---|---|
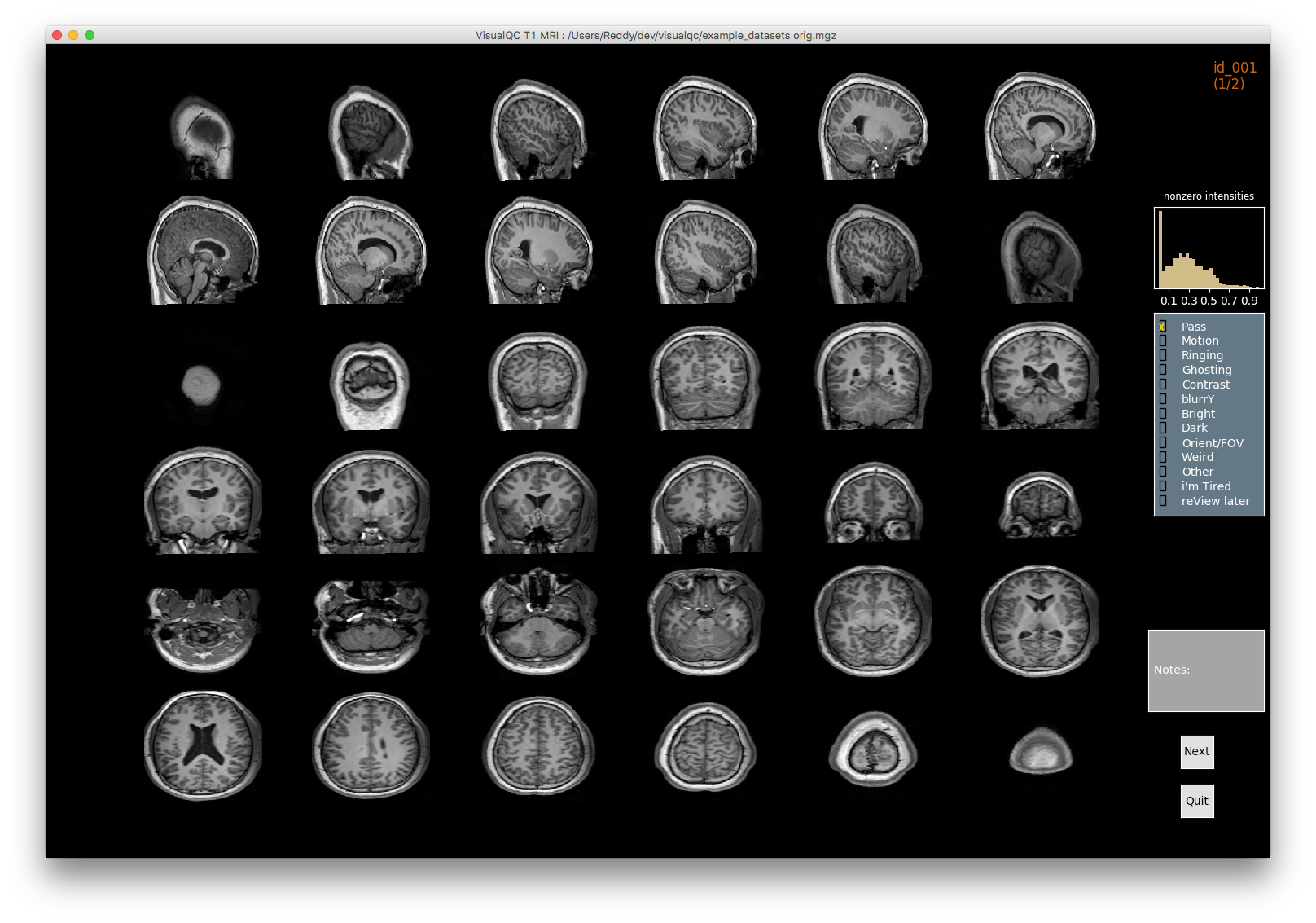 |
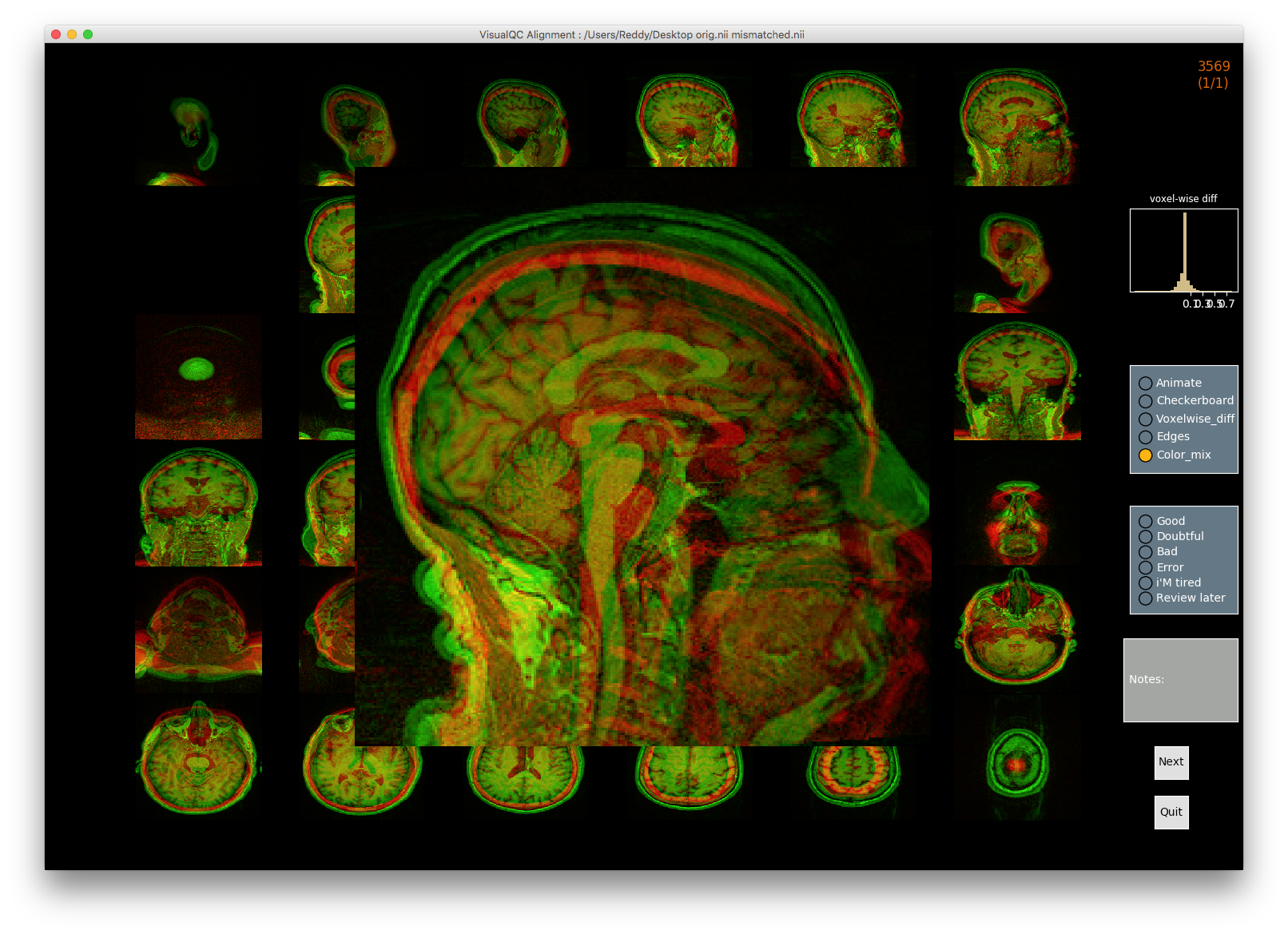 |
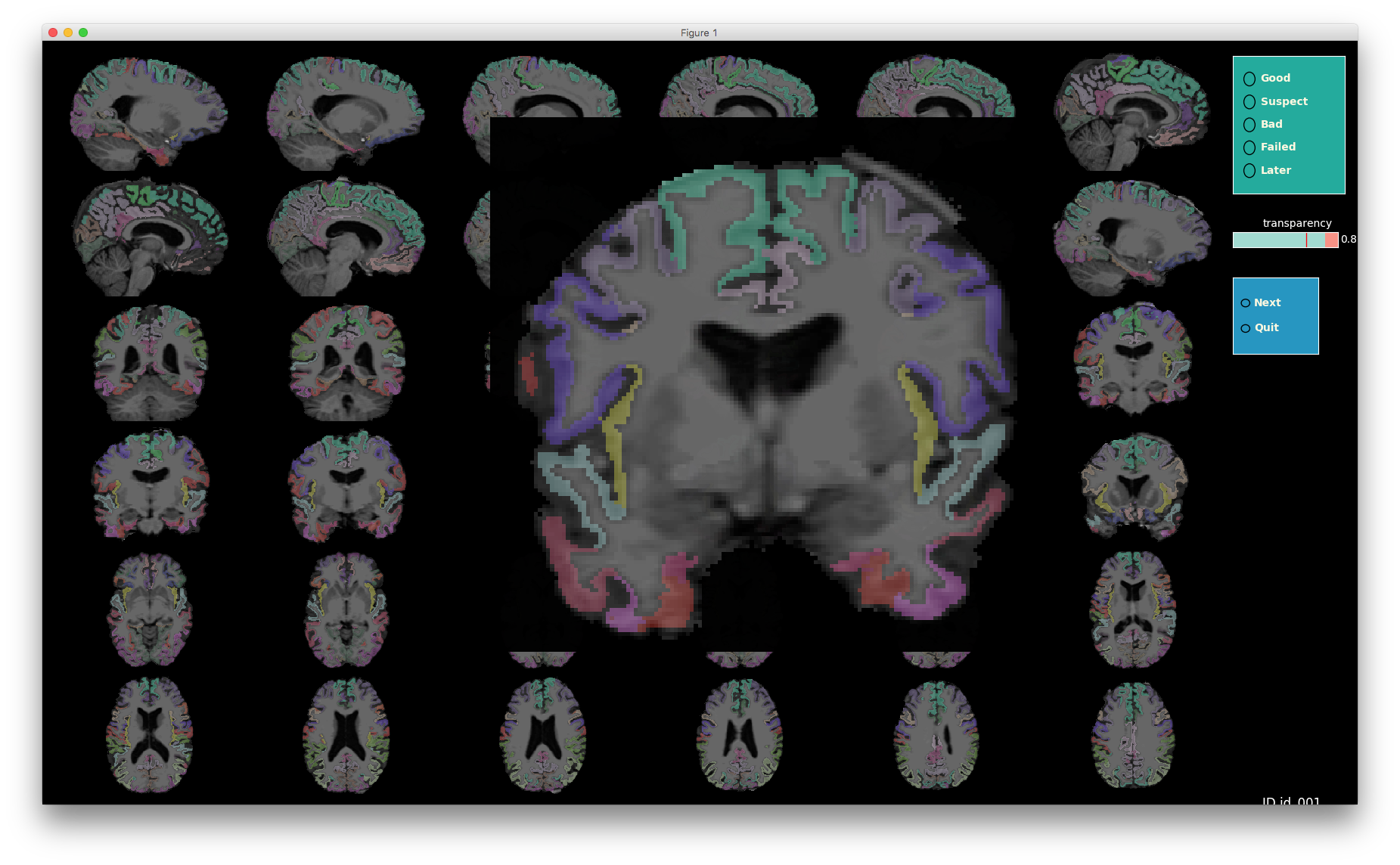 |
- Image processing failures happen! It is important to perform systematic quality control to minimize biases