sMRI Clean-up
Last updated on 2025-02-26 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- What are the sources of noise and artifacts in MR images?
- How do we extract/mask the brain?
Objectives
- Visualize bias fields and motion artifacts
- Generate brain masks
You Are Here!
Why do we need image clean-ups?
Correcting or cleaning-up certain artifacts from the raw (i.e. acquired) MR scans is crucial for the successful processing of subsequent image normalization tasks as well as the downstream statistical analyses. Some version (i.e. custom algorithm) of these two tasks is implemented in all commonly deployed processing pipelines such as FreeSurfer, FSL etc.
In this episode we will look at two common image clean-up tasks 1) Intensity normalization 2) Brain extraction.
Intensity normalization (a.k.a bias field correction; a.k.a. intensity inhomogeneity correction)
The bias field is a low-frequency spatially varying MRI artifact resulting from spatial inhomogeneity of the magnetic field, variations in the sensitivity of the reception coil, and the interaction between the magnetic field and the human body.
It causes a smooth signal intensity variation within tissue of the same physical properties.
The bias field is dependent on the strength of the magnetic field. If it is not corrected for 1.5T or higher MR scanners, it can considerably affect downstream analyses. Stronger magnets will induce higher bias.
-
Commonly used tools
- ANTs N4 bias correction (See figure below)
- FSL FAST (Note:FSL FAST is a multi-purpose segmentation tool that includes the bias field correction.)
Bias field correction quiz
What is the difference between bias field and image noise?
Bias field is modeled as multiplicative factor, whereas noise is typically assumed as additive and spatially independent (Gaussian) factor.
i.e. v(x) = u(x)f(x) + n(x), where v is the given image, u is the uncorrupted image, f is the bias field, and n is the noise.
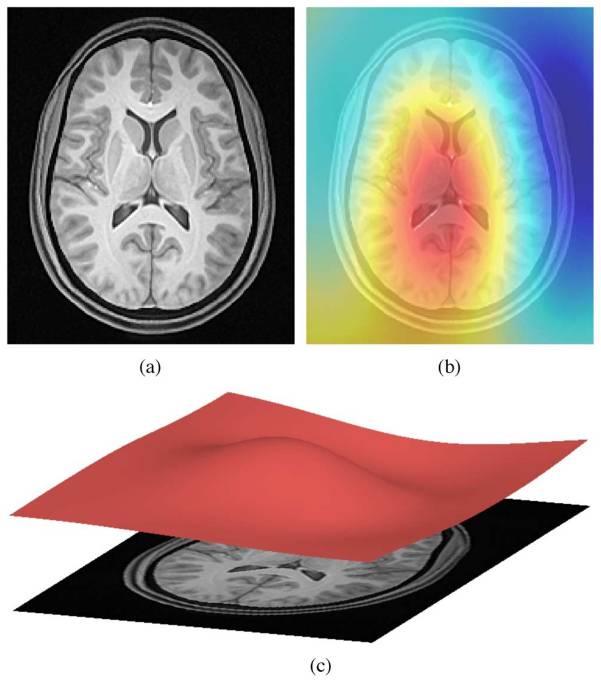
ANTs N4 correction
- Acquired T1w image (b) Estimated the bias field which can then be
used to “correct” the image. (c) Bias field viewed as a surface to show
the low frequency modulation.
Side-note: ANTs is a software comprising several tools and image processing algorithms. ANTs can be run independently or we can import ANTs scripts in python using nipype library.
PYTHON
n4 = N4BiasFieldCorrection()
n4.inputs.dimension = 3
n4.inputs.input_image = 'structural.nii'
n4.inputs.bspline_fitting_distance = 300
n4.inputs.shrink_factor = 3
n4.inputs.n_iterations = [50,50,30,20]
n4.cmdlineOUTPUT
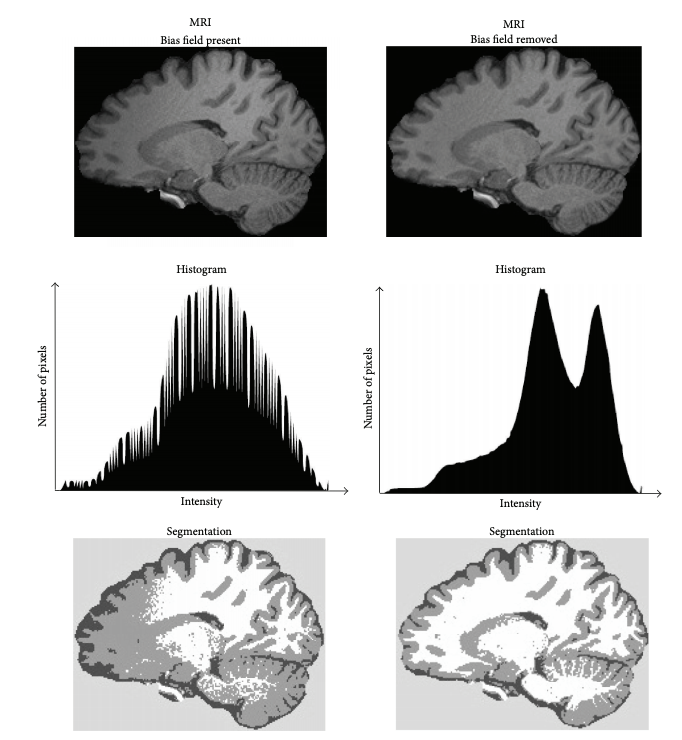
'N4BiasFieldCorrection --bspline-fitting [ 300 ] -d 3 --input-image structural.nii --convergence [ 50x50x30x20 ] --output structural_corrected.nii --shrink-factor 3'Impact of correction (source: Despotović et al.)
The top figure panel shows original and bias field corrected MR image slices. The middle figure panel shows the difference in the intensty histograms for the two image slices. And the bottom figure panel shows the impact of bias correction on a subsequent image segmentation task.
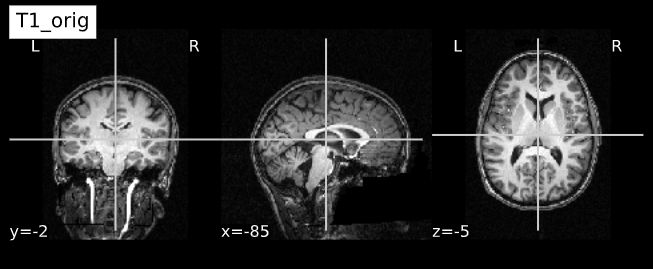
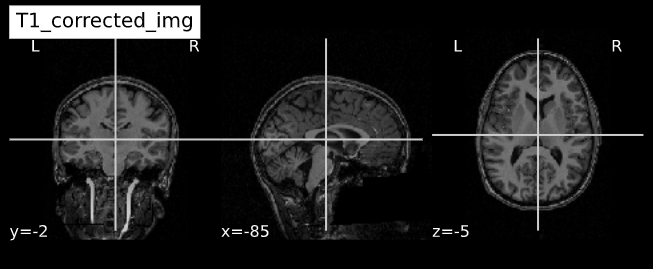
Visualizing “before” and “after”
PYTHON
T1_orig = subject_dir + 'orig.mgz'
T1_corrected = subject_dir + 'nu.mgz'
T1_img_orig = nib.load(T1_orig)
T1_img_corrected = nib.load(T1_corrected)
# plot
cut_coords = (-85,-2,-5)
plotting.plot_anat(T1_orig, title="T1_orig", cut_coords=cut_coords, vmax=255)
plotting.plot_anat(T1_corrected, title="T1_corrected_img", cut_coords=cut_coords, vmax=255)| Before | After |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Brain extraction (a.k.a skull-stripping)
Image contrasts from nonbrain tissues such as fat, skull, or neck can cause issues with downstream analyses starting with brain tissue segmentation.
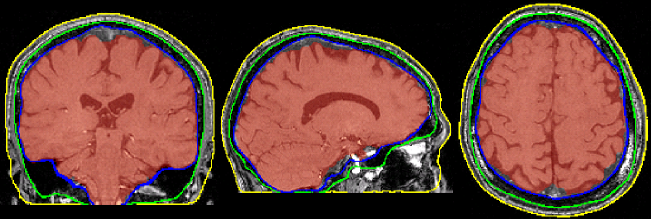
The brain extraction generates a mask that identifies brain voxels comprising grey-matter (GM), white-matter(WM), and Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures, including the brain stem and cerebellum.
The scalp, dura matter, fat, skin, muscles, eyes, and bones are classified as nonbrain voxels.
-
Commonly used tools
Note 1: At this point we are NOT trying to extract the brain sulci and gyri (i.e. cortical folds). We are just creating a simple brain mask for computational purposes, which need not capture the precise brain anatomy. Thus you may see some marrow and membrain included in the extracted brain.
Note 2: Brainstem and spinal cord are continuous so a rather arbitrarily cut-off point is selected.
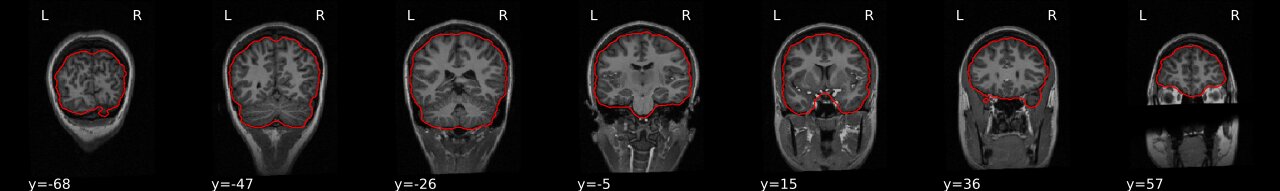
Example brain extractions pass / fail
| Pass | Fail |
|---|---|
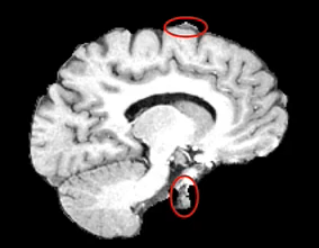 |
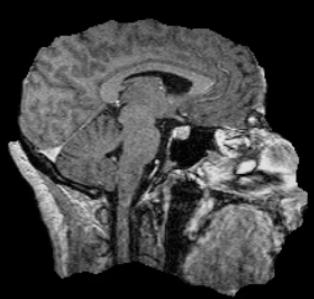 |
Source: FSL Introduction to Brain Extraction
Brain extraction quiz
Can we use this brain-mask as an estimate for brain volume?
Brain mask at this stage only offers a crude estimate about total brain volume. It can be used for quality control (e.g. detecting preprocessing algorithm failures). More accurate estimates of total brain and intracranial volumes are calculated in subsequent steps, which are used as covariates or normalizing factors in statistical analysis.
Side-note: ANTs is a software comprising several tools and image processing algorithms. ANTs can be run independently or we can import ANTs scripts in python using nipype library.
PYTHON
brainextraction = BrainExtraction()
brainextraction.inputs.dimension = 3
brainextraction.inputs.anatomical_image ='T1.nii.gz'
brainextraction.inputs.brain_template = 'study_template.nii.gz'
brainextraction.inputs.brain_probability_mask ='ProbabilityMaskOfStudyTemplate.nii.gz'
brainextraction.cmdlineOUTPUT
'antsBrainExtraction.sh -a T1.nii.gz -m ProbabilityMaskOfStudyTemplate.nii.gz
-e study_template.nii.gz -d 3 -s nii.gz -o highres001_'Visualizing “before” and “after” (see ../code/2_sMRI_image_cleanup.ipynb for detailed example.)
import nibabel as nib from nilearn import plotting
PYTHON
T1_normalized = subject_dir + 'T1.mgz'
T1_brain_extract = subject_dir + 'brainmask.mgz'
T1_img_normalized = nib.load(T1_normalized)
T1_img_brain_extract = nib.load(T1_brain_extract)
# plot
cut_coords = (-85,-2,-5)
plotting.plot_anat(T1_img_normalized, title="T1_img_normalized", cut_coords=cut_coords, vmax=255)
plotting.plot_anat(T1_img_brain_extract, title="T1_img_brain_extract", cut_coords=cut_coords, vmax=255)| Before | After |
|---|---|
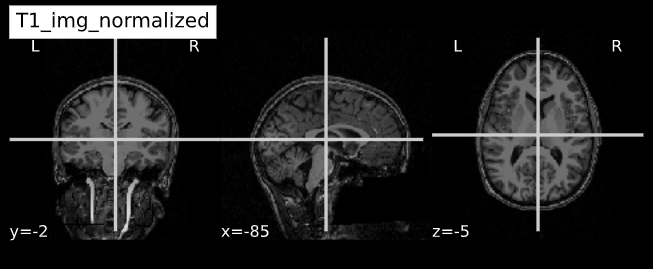 |
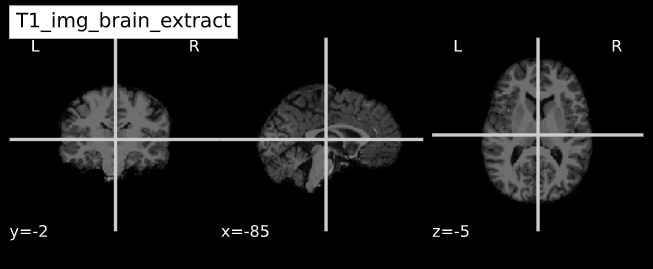 |
- Presence of artifacts can lead to flawed analysis and incorrect findings